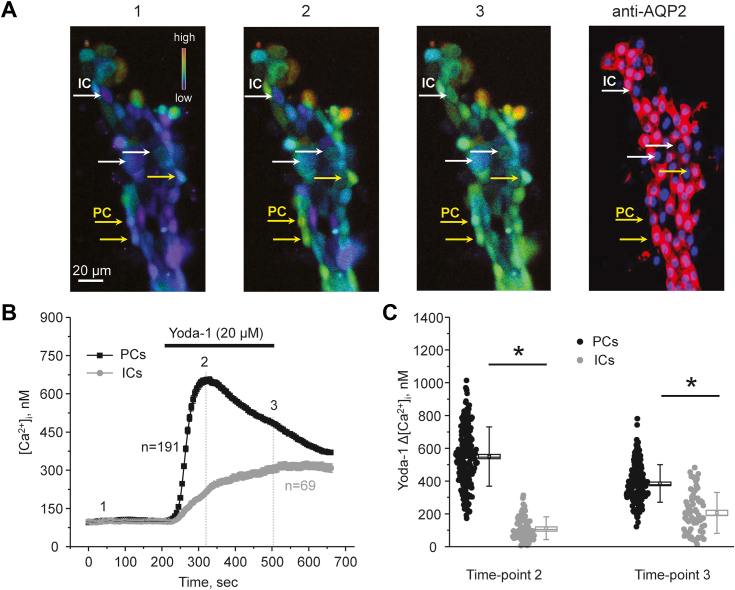
Figure 2.
A selective Piezo1 agonist, Yoda-1 induces different [Ca2+]iresponses in principal (PCs) and intercalated (ICs) cells of the collecting duct.A, representative pseudocolor images (blue-low and red-high) of an isolated split-opened collecting duct loaded with Ca2+-sensitive dye fura-2 at the baseline (1), after 30 s (2), and 5 min (3) of 20 μM Yoda-1 application. Shown on the right is confocal micrograph of the same split-opened collecting duct probed with anti-AQP2 (pseudocolor red) antibodies to discriminate PCs (highlighted with yellow arrows) and ICs (highlighted with white arrows). B, the averaged time courses of [Ca2+]i changes in PCs (black) and ICs (gray) upon application of Yoda-1 (shown with a bar on top). The time points shown in (A) are marked as 1 to 3. Number of individual cells is shown. Six different collecting ducts from three different mice were used for analysis. C, the summary graph comparing the magnitudes of Yoda-1-mediated [Ca2+]i elevations calculated as the difference in [Ca2+]i values before (time point 1), at the beginning (time point 2), and at the end (time point 3) of Yoda application in individual PCs and ICs from the conditions in A. Bars and whiskers represent SE and SD, respectively. Mean and median values are denoted with a dot and a line, respectively. ∗ - significant decreases (p < 0.05, one-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey test) between experimental groups shown with lines on the top. AQP2, aquaporine 2.