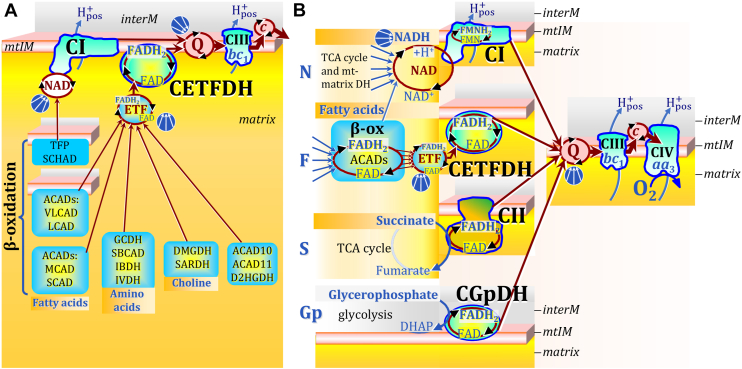
Figure 4.
Convergent electron transfer into the NAD junction, ETF junction, and Q-junction indicated by convergent arrows, without showing the alignment of supercomplexes. Inter-membrane space (interM) indicated in grey and mt-matrix in yellow-orange. A, convergent FAD-linked electron transfer into the ETF junction as the first step in β-oxidation from very long- and long-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenases (ACADS, membrane-bound), medium-, and short-chain ACADs including short/branched-ACAD (SBCAD) and Complex I assembly factor ACAD9; in branched-chain amino acid oxidation from glutaryl-CoA DH (GCDH), SBCAD, isobutyryl-CoA DH (IBDH) and isovaleryl-CoA DH (IVDH); in choline metabolism from dimethylglycine DH (DMGDH) and sarcosine DH (SARDH); and from acyl-CoA DH family members 10 and 11 (ACAD10, ACAD11) and D-2-hydroxyglutarate DH (D2HGDH). References (357, 360, 361). ETF is the redox shuttle feeding electrons into the membrane-bound electron transferring flavoprotein Complex (CETFDH on the matrix side of the mtIM) and further into Q. Steps two to four in β-oxidation of long- and medium-chain fatty acids are catalyzed by trifunctional protein (TFP, membrane-bound). Step three reduces NAD+ to NADH + H+, feeding electrons into the NAD-cycle, catalyzed by TFP and short-chain 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase (SCHAD). B, N: N-pathway through Complex I (CI; see Fig. 1). F: F-pathway of fatty acid oxidation through the β-oxidation cycle (β-ox) with ACADs binding noncovalently FAD; converging electron transfer through ETF to CETFDH, and dependence on the N-pathway. S: S-pathway through CII. Gp: Gp-pathway through mt-glycerophosphate DH Complex (CGpDH on the inter-membrane side of the mtIM) oxidizing glycerophosphate to dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) in the inter-membrane space.