Figure 2. Deletion of Piezo2 in TSCs and lamellar cells does not affect light touch responses in Aβ sensory neurons.
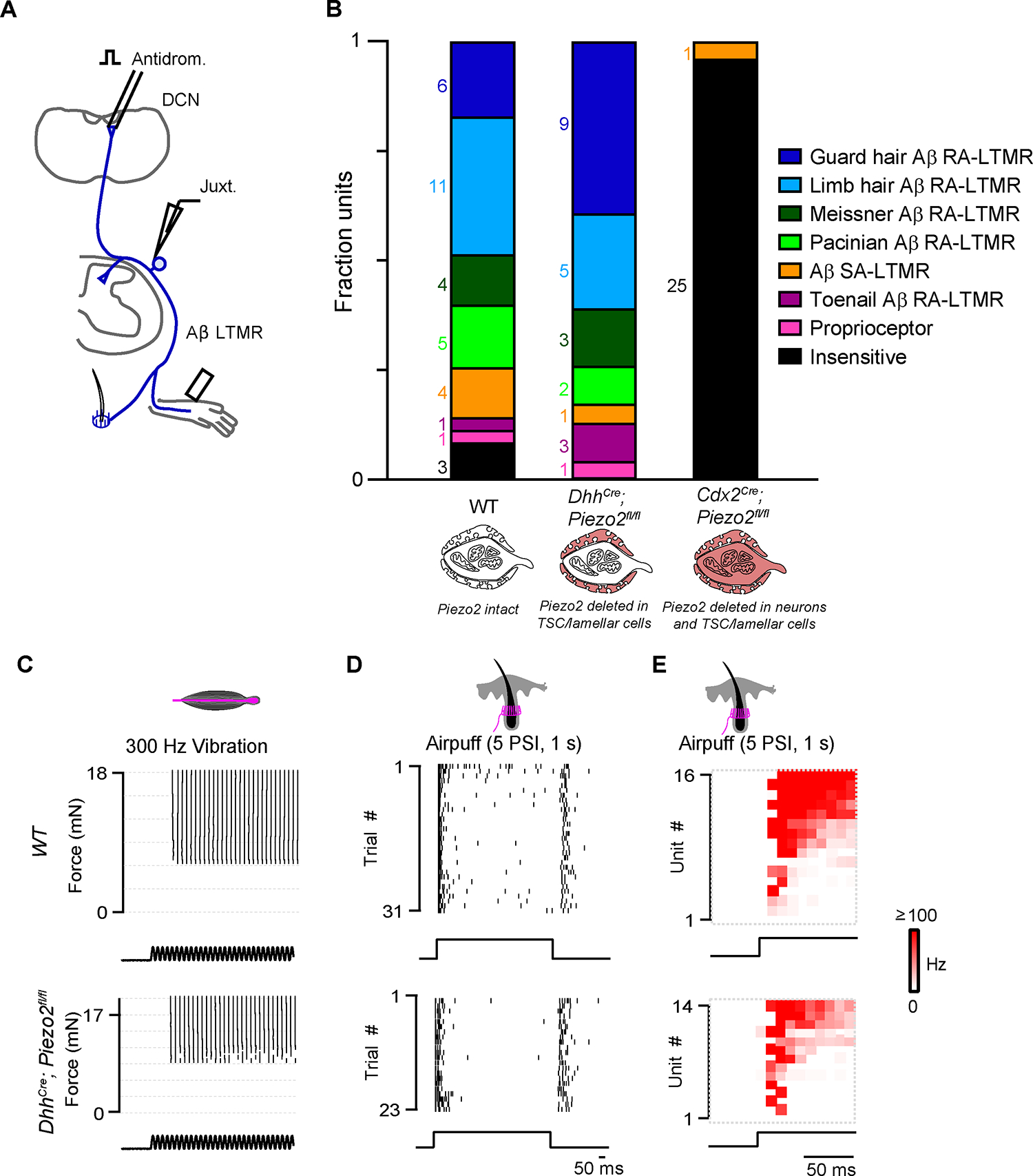
(A) Schematic of juxtacellular recordings. Aβ sensory neurons were identified with antidromic activation of the dorsal column nucleus (DCN) or dorsal column (DC). Mechanical stimuli were applied to the hindpaw and hairy thigh.
(B) The fraction of DCN-projecting units identified as a specific sensory neuron class based on the location of receptive field and response to low-threshold mechanical stimuli in wild type (wt) animals (n=3), DhhCre;Piezo2fl/fl mice (n=3), and Cdx2Cre;Piezo2fl/fl mice (n=2).
(C) Raster of single Pacinian Aβ RA-LTMR responses to vibration (300 Hz) at different forces in a wt (top) and a DhhCre;Piezo2fl/fl animal (bottom).
(D) Same as in (C) but for hairy skin Aβ RA-LTMR responses to air puff.
(E) Histograms of air puff responses for all Aβ hairy units activated by DCN stimulation in wt (top) and DhhCre;Piezo2fl/fl animals (bottom). In wt animals, 15/16 hairy units were air puff-sensitive. In the DhhCre;Piezo2fl/fl animals, 14/15 hairy units were air puff-sensitive. See also Figure S3.
