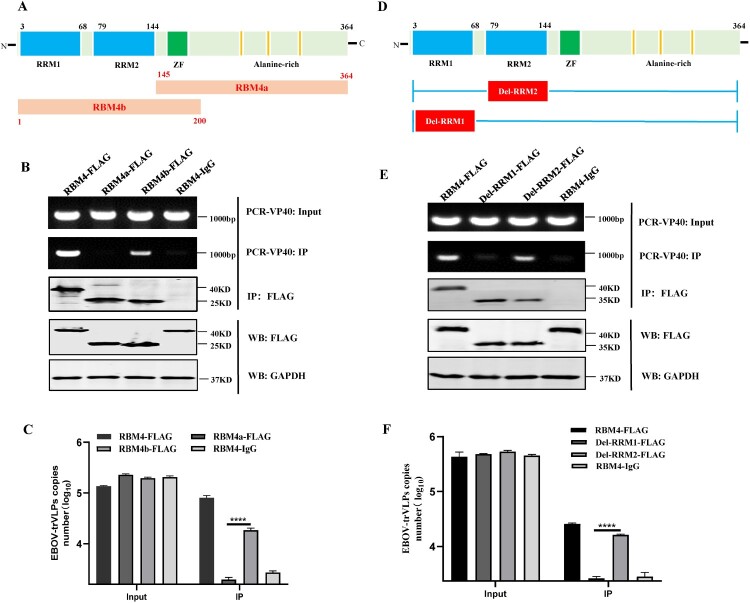
Figure 4.
The N-terminal region RRM1 of RBM4 is the key domain in interacting with EBOV genome. (A) Schematic of two RBM4 mutants including N-terminal RBM4b and C-terminal RBM4a. (B–C) The plasmids encoding RBM4-FLAG, RBM4a-FLAG and RBM4b-FLAG were transfected with HEK293T cells. At 24 h p.t., EBOV-trVLPs assay were performed. At 72 h p.t., expression of RBM4 or its truncations and viral genome in cells were detected by WB and PCR, respectively. Then, the interaction between RBM4 or its truncations and viral genome was detected using RIP assay. (D) Schematic of two RBM4 mutants including delRRM1 with deleting RRM1 domain and delRRM2 with deleting RRM2 domain. (E–F) The plasmids encoding RBM4-FLAG, delRRM1-FLAG and delRRM2-FLAG were transfected with HEK293T cells. At 24 h p.t., EBOV-trVLPs assay was performed. At 72 h p.t., expression of RBM4 or its truncations and viral genome in cells were detected by WB and PCR, respectively. Then, the interaction between RBM4 or its truncations and viral genome was detected using RIP assay. The mean and SEM from one representative experiment (n = 3) of 3 independent experiments are indicated. ****P < 0.0001 (two-tailed Student t-test).