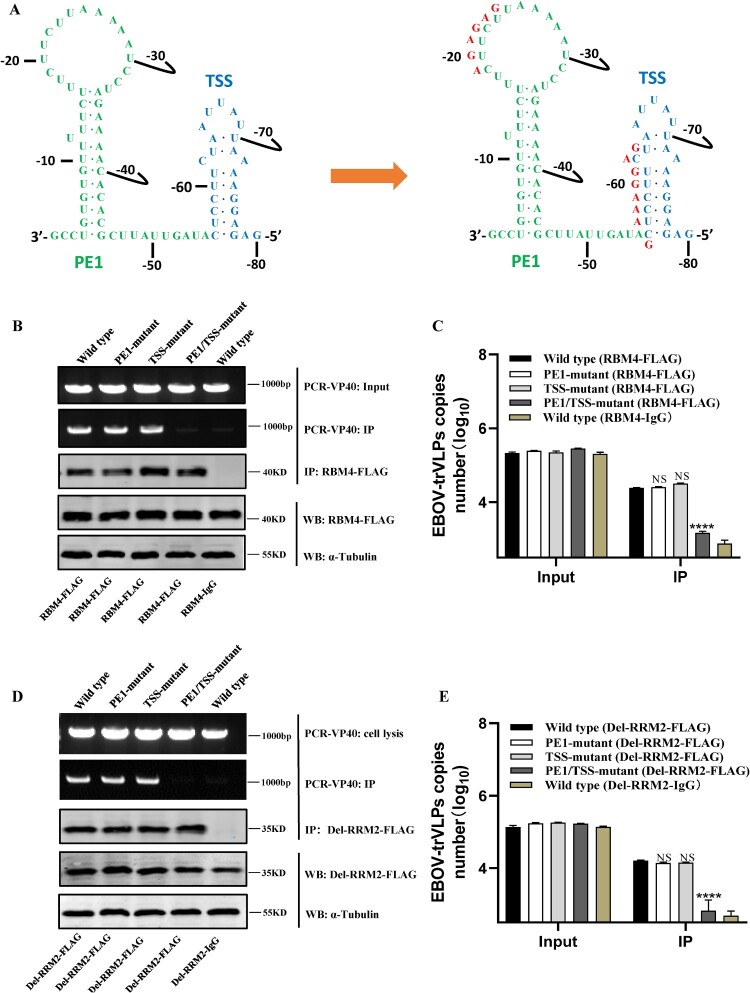
Figure 5.
The “CU” enrichment elements of 3′-leader region of viral genome are crucial for interacting with RBM4. (A) Schematic of viral genome 3′-leader region, and its mutant which replacing the “CUUCUU” sequence of PE1 and “CUCCUUCU” sequence of TSS with “AGAGAG” and “GAAAGGAG.” (B–C) HEK293T cells were transfected with pCAGGS-RBM4-FLAG. Twenty-four hours later, cells were transfected with plasmids encoding NP, VP35, VP30, L, p4cis-vRNA-RLuc or p4cis-vRNA-RLuc-mutant. At 24 h p.t., supernatants were discarded and replaced with fresh medium. At 48 h p.i., expression of RBM4-FLAG and viral genome or its mutants in cells were detected by WB and PCR, respectively. Then, the interaction between RBM4-FLAG and viral genome or its mutants was detected using RIP assay. (D–E) HEK293T cells were transfected with pCAGGS-Del-RRM2-FLAG. Twenty-four hours later, cells were transfected with plasmids encoding NP, VP35, VP30, L, p4cis-vRNA-RLuc or p4cis-vRNA-RLuc-mutant. At 24 h p.t., supernatants were discarded and replaced with fresh medium. At 48 h p.i., expression of Del-RRM2-FLAG and viral genome or its mutants in cells were detected by WB and PCR, respectively. Then, the interaction between Del-RRM2-FLAG and viral genome or its mutants was detected using RIP assay. The mean and SEM from one representative experiment (n = 3) of 3 independent experiments are indicated. ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001 (two-tailed Student t-test). NS, not significant.