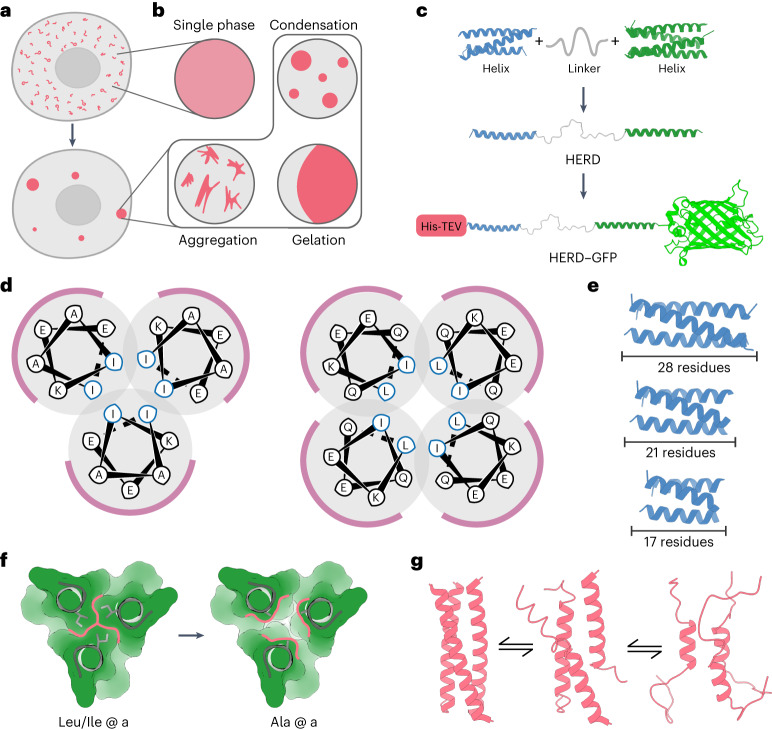
Fig. 1. Design and assembly of de novo polypeptides for biomolecular condensation.
a, Cartoon for membraneless-organelle formation in cells, that is, protein condensation leading to the formation of de-mixed droplets. b, Protein solutions can form a single phase, or phase-separated systems including condensates, aggregates and gels. c, HERD design strategy for phase separation by concatenation of de novo CCs. d, Helical wheels of the heptad (seven-residue) repeats for trimeric (left) and tetrameric (right) CCs with hydrophobic interface residues in blue and solvent-exposed residues in black. e–g, Weakening of PPIs by truncating the helical CC lengths (e), disrupting packing in the hydrophobic core through Ile/Leu (left) to Ala (right) mutations to the a position in the abcdefg heptad repeat (f) and reducing helical propensity by replacing surface residues to those with a low helical propensities (g).