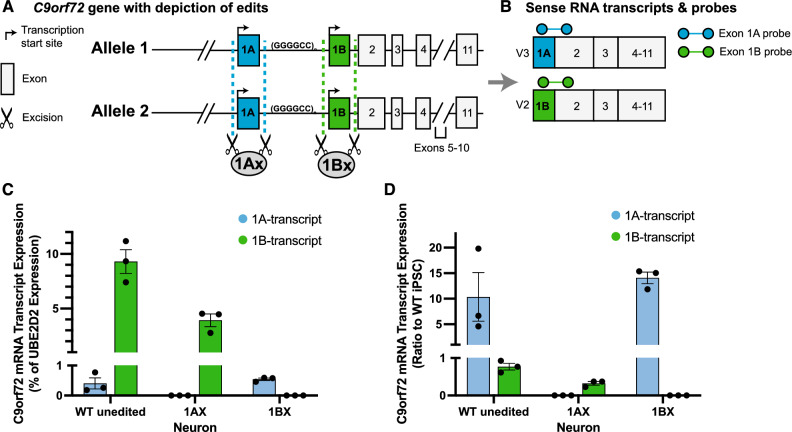
Figure 4.
Knock-out validated ddPCR probes to measure 1A- and 1B-containing C9orf72 mRNA. (A) We generated a selective excision of either exon 1A and exon 1B on both alleles to measure the specificity of exon-spanning ddPCR probes (from Table S1). We could not measure variant 1 mRNA given low abundance of this transcript in iPSC derived neurons. (B) Probes spanning exon 1A-2 (blue) and 1B-2 (green) measured 1A-containing mRNA (variant 3, V3) and 1B-containing mRNA (variant 2, V2). (C) We quantified mRNA in 2-week-old neurons from our WT, exon 1A-excised (1Ax) and exon-1B excised (1Bx) clonal cell lines. Exon 1A-2 probe is specific for 1A-transcripts and exon 1B-2 probe is specific for 1B-transcripts. Most of the transcripts in the cell derive from exon 1B. (D) We calculated the transcript expression change for motor neurons derived from each line compared to WT iPSC levels. Although exon 1B-transcripts are the most abundant, levels are equivalent between WT iPSCs and motor neurons (Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test, p = 0.13). However, 1A transcripts increased 10–15 fold compared to iPSCs (Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test, p = 0 < 0.01 for WT neurons and p < 0.001 for 1Bx neurons). Dots = biological replicates. Error bar = SEM.