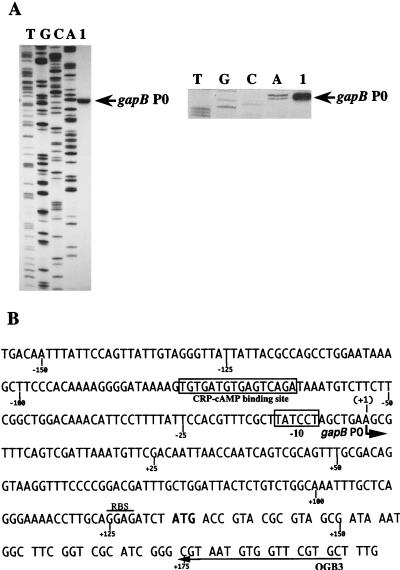
FIG. 2.
Localization of the in vivo gapB transcription start site. (A) Primer extension was performed with oligonucleotide OGB3 and with total RNA extracted from TG1 cells grown on M63 medium supplemented with glucose as the sole carbon source (lane 1). Total RNA extraction and primer extension were performed as described in Materials and Methods. Markers (lanes A, C, G, and T) were made by sequencing plasmid pPBK100 with oligonucleotide OGB3 and T7 DNA polymerase. The position of the initiation site is indicated (gapB P0) on the gel autoradiogram (left) and on the enlargement of the area corresponding to the initiation site (right). (B) DNA sequence of the transcriptional regulatory region of the E. coli gapB gene (2). The in vivo transcription initiation site gapB P0 identified in panel A is marked with a bent arrow. The first nucleotide of the gapB mRNA is numbered +1 (the preceding one is numbered −1). The −10 region and the CRP-cAMP binding sequence are boxed. The arrow labeled OGB3 shows the sequence which is complementary to the primer oligonucleotide used for primer extension analysis. The ribosome binding sequence (RBS) is overlined.