Figure 4. Crystal structure of inter-dimer-epitope antibody rhMZ100-C Fab in complex with ZIKV E glycoprotein.
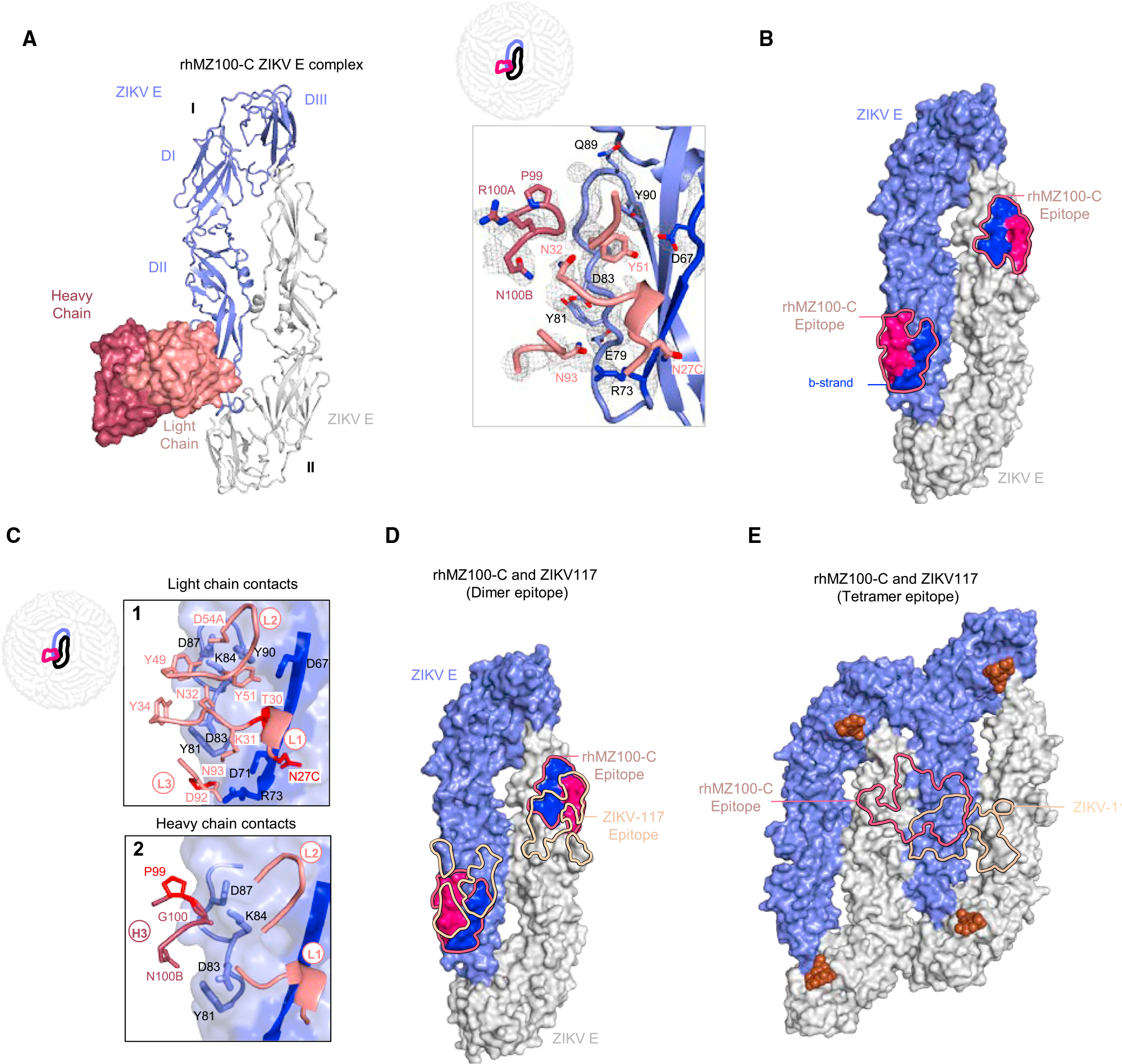
(A) Left: top view of the co-crystal structure of rhMZ100-C in complex with ZIKV E (PRABC59). rhMZ100-C Fv heavy and light chains are colored dark and light raspberry, respectively, and are shown in surface representation, while two ZIKV E protomers are shown in ribbon representation colored blue and gray. ZIKV E protomers, left to right, are labeled as I and II. Right: 2Fo-Fc electron density for the rhMZ100-C and ZIKV E interface residues is shown as gray mesh (contoured at 1.5σ).
(B) Epitope footprint of rhMZ100-C antibody is indicated with a solid raspberry-colored line displayed on two ZIKV E protomers (surface representation). Relevant antigenic ZIKV E regions within the epitope are labeled (b strand is shown in blue and rest of the rhMZ100 epitope is shown in raspberry color).
(C) rhMZ100-C contact residues are shown as sticks based on (1) CDRs L1, L2, and L3; (2) CDR H3 antibody-contacting regions; b strand residues 63–73 on protomer I are highlighted in dark blue color. SHM residues are colored bright red.
(D) Epitopes for rhMZ100-C and ZIKV-117 antibodies are represented with raspberry and teal colored lines, respectively. ZIKV-117 (PDB: 5UHY) antibody was overlaid onto the rhMZ100-C ZIKV E structure to map the epitope.
(E) rhMZ100-C and ZIKV-117 epitopes are mapped onto a ZIKV E-tetramer (PDB: 5IRE).
See also Figures S3–S5 and Tables S4 and S5.
