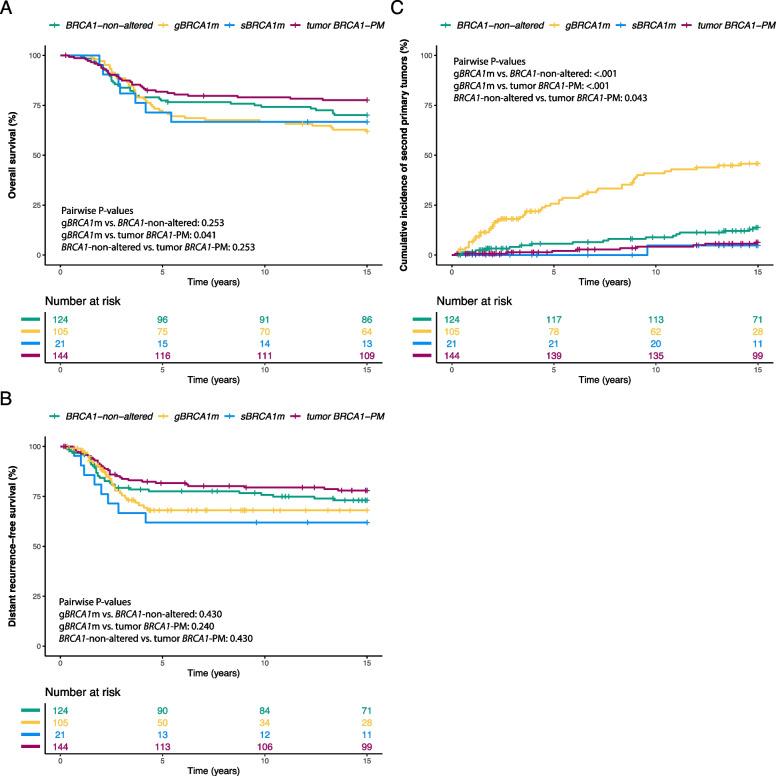
Fig. 3.
Clinical outcomes according to BRCA1 status. Clinical outcomes include (A) overall survival, (B) distant recurrence-free survival, and (C) cumulative incidence of second primary tumors. Log-rank tests and Gray’s tests were used to compute the pairwise P-values. Comparison was only made among germline BRCA1-mutated, tumor BRCA1 promoter-methylated, or BRCA1-non-altered patients, as the number of somatic BRCA1-mutated patients was too low. Pairwise P-values were corrected for multiple testing using the Benjamini–Hochberg procedure. The uncorrected P-values for overall survival comparison are as follows: gBRCA1m vs. BRCA1-non-altered (P-value = 0.253), gBRCA1m vs. tumor BRCA1-PM (P-value = 0.014), and tumor BRCA1-PM vs. BRCA1-non-altered (P-value = 0.189). The uncorrected P-values for distant recurrence-free survival comparison are as follows: gBRCA1m vs. BRCA1-non-altered (P-value = 0.429), gBRCA1m vs. tumor BRCA1-PM (P-value = 0.079), and tumor BRCA1-PM vs. BRCA1-non-altered (P-value = 0.328). The uncorrected P-values for the incidence of second primary tumors comparison are as follows: gBRCA1m vs. BRCA1-non-altered (P-value < 0.001), gBRCA1m vs. tumor BRCA1-PM (P-value < 0.001), and tumor BRCA1-PM vs. BRCA1-non-altered (P-value = 0.043). Abbreviations: BRCA1-non-altered, without germline BRCA1 mutation, without somatic BRCA1 mutation, and without tumor BRCA1 promoter methylation; gBRCA1m, germline BRCA1 mutation; sBRCA1m, somatic BRCA1 mutation; tumor BRCA1-PM, tumor BRCA1 promoter methylation. Note that at time 0, the numbers at risk of tumor BRCA1 promoter methylated patients and BRCA1-non-altered patients were not 146 and 127, respectively, because five germline BRCA2-mutated patients were removed