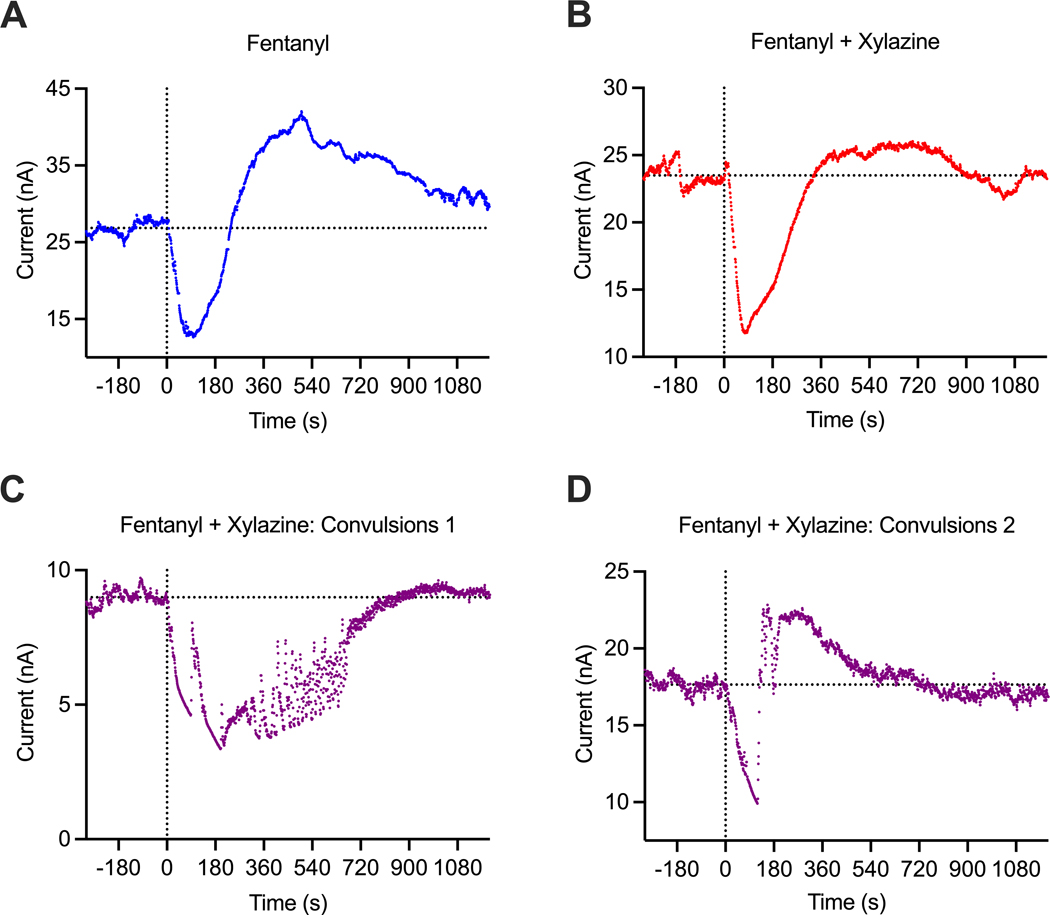
Figure 4.
Primary data examples of changes in electrochemical currents (nA) induced by fentanyl and fentanyl-xylazine mixture in freely moving rats. A = fentanyl alone (20 ug/kg), B = fentanyl (20 ug/kg)+xylazine (1 mg/kg), typical example; C and D = unusual changes induced by fentanyl-xylazine mixture with convulsions. Values of reduction current are shown with original (1-s) time resolution, and they were inverted. Since basal reduction currents widely varied between sensors, data were analyzed as the change relative to basal value=100%. Convulsions were never seen after fentanyl alone, but they occurred in 3 cases (in 2 rats) after injections of fentanyl-xylazine mixture.