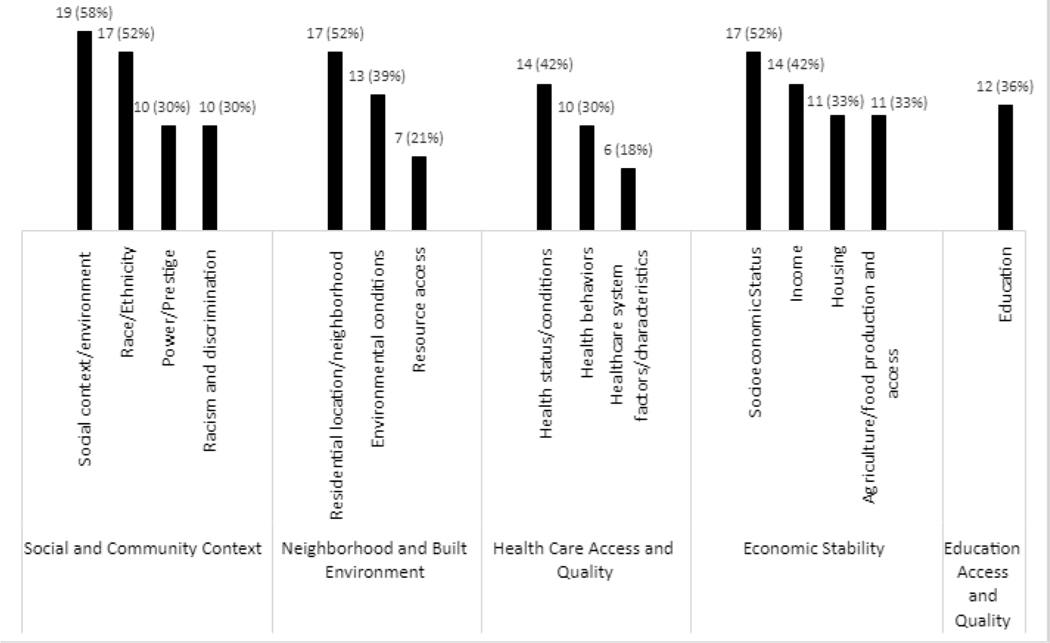
Fig. 1. Top Three Social Determinants of Healtha and Individual Factors Most Frequently Identified in Health Equity Guiding Frameworks Categorized by Healthy People 2030 Key Domainsb-d (N =33).
a Social determinants of health (SDOHs) are broader in scope and include the social, economic, and environmental factors that influence the health and well-being of communities. SDOHs and individual factors can be categorized in the five different domains in the Healthy People 2030 model: Economic Stability, Education Access and Quality, Health Care Access and Quality, Neighborhood and Built Environment, and Social and Community Context.
b Includes health equity frameworks found in Table 1.
c Only one SDOH was categorized in the Education Access and Quality domain, therefore only one is shown.
d Definitions for select terms:
Agriculture/food production and access addresses “supply side” of food security at the national or international level and is determined by economic and physical access factors such as the level of food production, stock levels, and net trade (this includes food access, which refers to household level food security and whether individuals can obtain food, food stability, food availability, food deserts, rurality, agriculture and food production).
Healthcare system factors/characteristics refers to access to quality, affordable, and timely preventive and curative health care that recognizes individual patient needs, including their health history and personal preferences.
Power/Prestige refers to an imbalance in status and opportunities between populations based on factors such as race and ethnicity, gender, income, or sexual orientation.
Social context/environment are factors and circumstances in the broader social setting (such as exposure to community stressors or personal/life experiences) that shape behaviors, beliefs, and/or perceptions of individuals and groups of people.