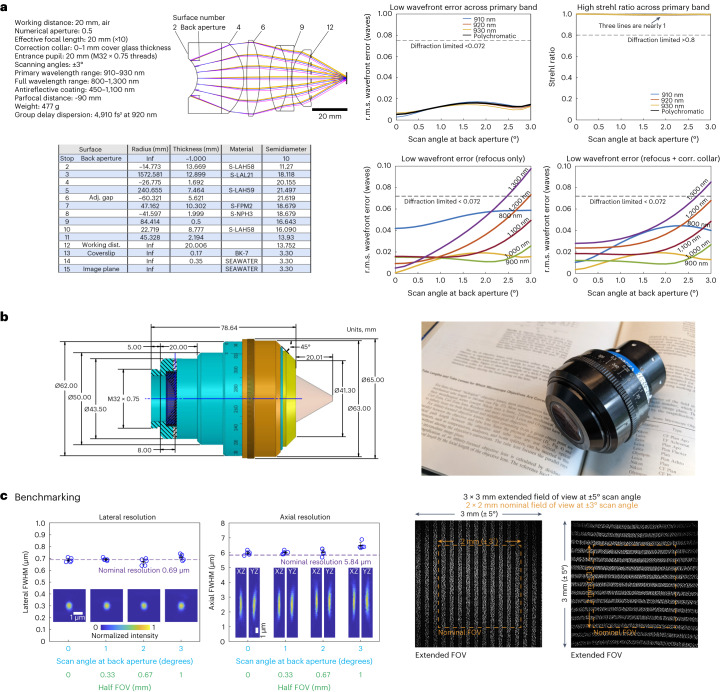
Fig. 1. Design and benchmarking.
a, Left: the specifications that constrained the design to ensure compatibility with two-photon imaging systems that are typically used in vivo. The resulting optical design has six elements and one adjustable air gap (adjustment range 5.4–6.0 mm) to optimize performance. The full lens prescription is provided. Right: the primary optimizations were for 920 ± 10 nm for two-photon excitation of GFP-based indicators. The optical model predicts low r.m.s. wavefront errors and high Strehl ratios for 910, 920 and 930 nm light across the scan angles of 0–3°, well beyond the diffraction limit. Performance is also diffraction-limited across a broader wavelength range from 800 to 1,300 nm. The r.m.s. wavefront error remains below the diffraction limit for most of the 0–3° scan angle range, when the focal plane is allowed to naturally shift with wavelength, and the correction (corr.) collar provides an additional degree of optimization. b, Left: the mechanical design of the objective prioritized keeping the widest diameter near the middle of the objective to avoid mechanical collisions with objective mounts. All dimensions are in mm unless otherwise noted. Right: a photograph of the manufactured objective. c, Left: two-photon excitation PSF measurements were made with 0.2 µm beads embedded in agar at a depth of 350 µm. The excitation wavelength is 910 nm. z stack images are acquired for beads at four lateral locations including on axis, 1°, 2° and 3° off axis (n = 5 beads at each location). FWHM of the Gaussian fits for measurements (mean values ± s.d.) indicate lateral and axial resolutions indistinguishable from diffraction-limited resolutions. The pixel size of the images is 0.058 × 0.064 × 0.69 µm3 (xyz). Right: images of a fluorescent calibration sample with a periodic line pattern (five lines per millimeter) in two orientations acquired under a ±5° scan angle show a nominal 2 × 2 mm2 FOV of the objective under the ±3° scan angle, and a 3 × 3 mm2 FOV under ±5° scan angle.