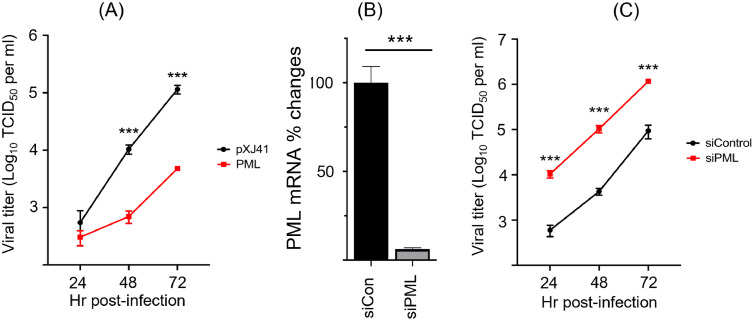
Fig. 4.
Restriction of PRRSV replication by PML. (A), Suppression of PRRSV replication in PML-overexpressing cells. Plasmids containing the genes for six individual isoforms of PML were equally mixed and transfected to MARC-145 cells for overexpression. At 48 h of PML expression, cells were infected with PRRSV at 1 multiplicity of infection (MOI) for indicated times. Culture supernatants were collected at 24, 48, and 72 h post-infection, and viral titers were determined by TCID50. (B), siRNA-mediated gene silencing of PML as indicated as PML mRNA% changes (Y axis). MARC- 145 cells were grown to 50 % confluence in 6-well plates, and 100 pmol of siRNA per well was transfected using Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA). At 48 h of siRNA treatment, total cellular RNA was extracted and subjected to RT-qPCR using PML-specific primers as described in Materials and Methods. (C), Enhanced replication of PRRSV in PML-knockdown cells. Endogenous PML gene expression was knockdown using siRNAs for 48 h as described above (B), and PML-knockdown cells were infected with PRRSV at 1 MOI. Culture supernatants were collected at 24, 48, and 72 h, and viral titers in the culture supernatants were determined by TCID50. pXJ41, empty vector; Red lines indicate PRRSV titers in PML-overexpressing cells (A) or PML-siRNA (siPML)-treated cells (C). Black lines indicate PRRSV titers in cells treated with control siRNA. Error bars represent means ± standard deviation. The experiments were repeated three times (n = 3). ***, P<0.001.