Fig. 2. Bacterial phylogenies derived from children’s microbiomes and strain sharing with their mothers.
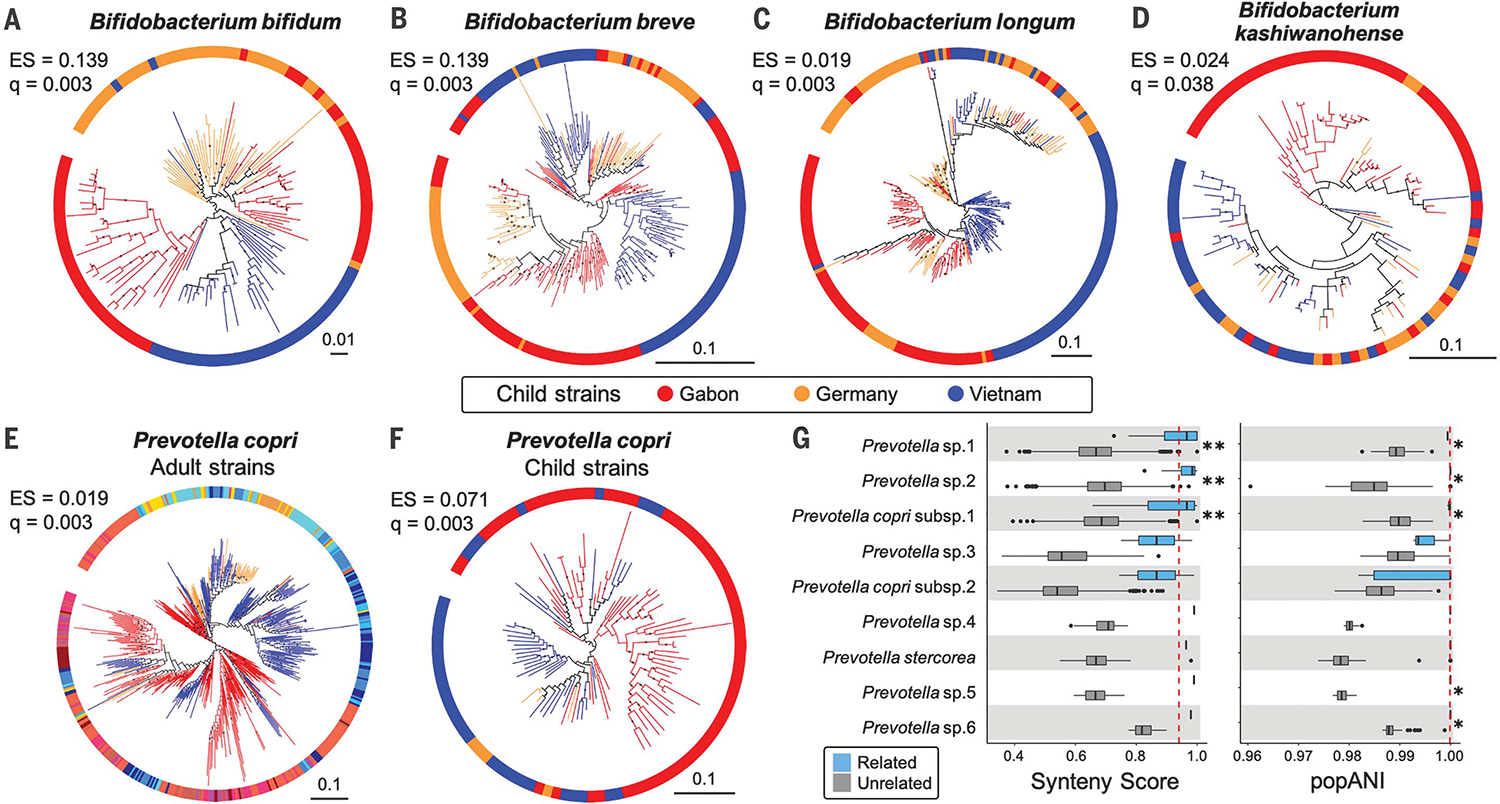
(A to D) Four species of Bifidobacterium show evidence of cophylogeny based on mothers’ genotypes. (E) Phylogeny of P. copri strains in adults and (F) in children. The colors in (E) correspond to those in Fig. 1B. Bootstrap values ≥50% are shown as black dots on branches, and the phylogenies are rooted at the midpoint. The scales show substitutions per site. (G) Prevotella strain sharing between mothers and their own children (“related,” blue boxplots) compared with sharing between women and unrelated children (“unrelated,” gray boxplots). (Left) Strain comparisons using SynTracker (39). (Right) Strain comparisons using inStrain (40). Dashed red lines indicate the thresholds for strain sharing events [0.96 for synteny; 0.99999 for popANI (population-level average nucleotide identity)]. *P < 0.05 and **P < 5 × 10−5 using Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney test. Codiversification test results for all 20 common child taxa are reported in table S11.
