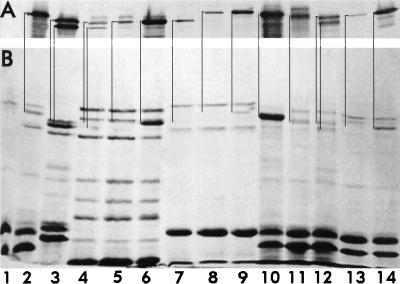
FIG. 4.
Chromosome- and plasmid-expression of FepA and its homologs. Outer membranes were prepared by Sarkosyl extraction of cell envelopes from bacteria grown in MOPS minimal medium, subjected to SDS-PAGE, and either stained with Coomassie blue (B) or transferred to nitrocellulose and stained with anti-FepA monoclonal antibodies 2, 27, 45, (30), goat anti-mouse immunoglobulin-alkaline phosphatase, and nitroblue tetrazolium-bromochloroindolyl phosphate (7) (A). E. coli KDF541 (lane 1) and BN1071 (lane 2), S. typhimurium Enb7 (lane 3), P. aeruginosa K407 (lane 4) and K201 (lane 5), and B. bronchisepticus 19387 (lane 7) and 19385 (lane 8) were cultured in iron-deficient MOPS medium. Strains K201 and 19385 were also grown in MOPS medium containing enterobactin (2 μM; lanes 6 and 9, respectively). Outer membranes from KDF541, grown in MOPS medium and harboring either pITS449 (EcoFepA; lane 10), pENB5 (StyFepA; lane 11), pTY994 (StyIroN; lane 12), pKP1 (BpeFepA; lane 13), or pCD3 (PaeFepA; lane 14) were also analyzed. Immunoreactive bands in the immunoblot correspond to the indicated stained bands in the SDS-PAGE gel.