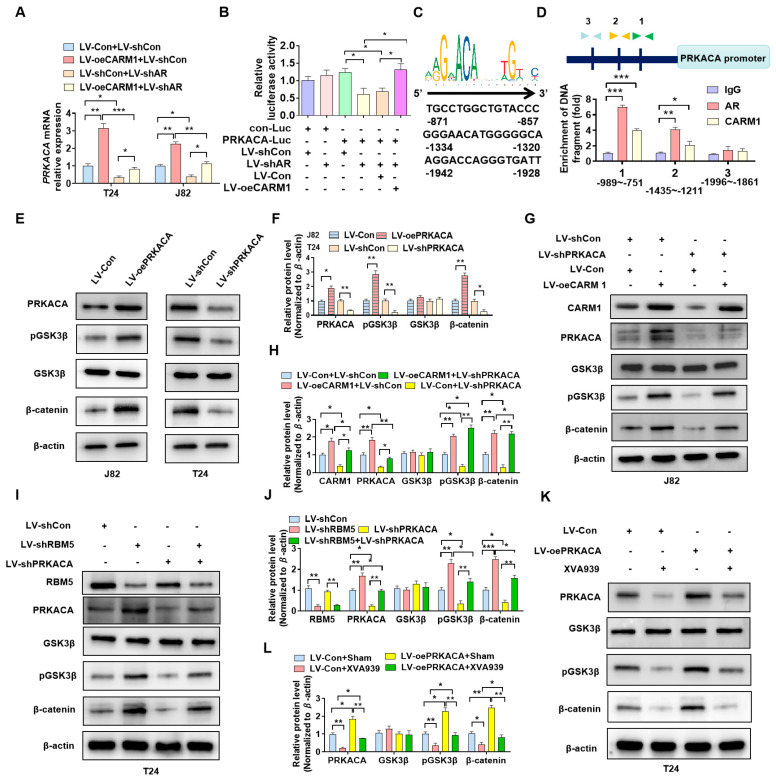
Figure 6.
PRKACA is involved in CARM1−promoted GSK3β phosphorylation. (A) T24 and J82 cells were transfected with LV−oeCARM1 and LV−shAR, and RT–qPCR was used to detect PRKACA mRNA expression. (B) The dual luciferase reporter gene assay revealed that CARM1 and androgen receptor (AR) coregulated PRKACA promoter activity. (C) Analysis of the potential AR−CARM1 cobound motif on the promoter of the PRKACA gene. (D) ChIP–PCR was performed to verify the binding sites of AR and CARM1 on the PRKACA promoter using AR and CARM1 antibodies. (E,F) Cells were transfected with the indicated lentiviruses, and western blotting was performed to assess the expression of p-GSK3β, GSK3β, and β-catenin. (G,H) J82 cells were transfected with LV−shPRKACA or LV−oeCARM1 alone or in combination, and the protein levels of p-GSK3β, GSK3β, and β-catenin were measured via western blotting. (I,J) In T24 cells, RBM5 and PRKACA, alone or in combination, were knocked down by lentivirus, and western blotting was performed to detect the expression of p-GSK3β, GSK3β, and β-catenin. (K,L) T24 cells were transfected with LV−PRKACA or LV−Con and then treated with XVA939, a Wnt/β-catenin pathway inhibitor. Western blotting was performed to evaluate the protein levels. All data were derived from three independent experiments and expressed as the mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 vs. their corresponding controls.