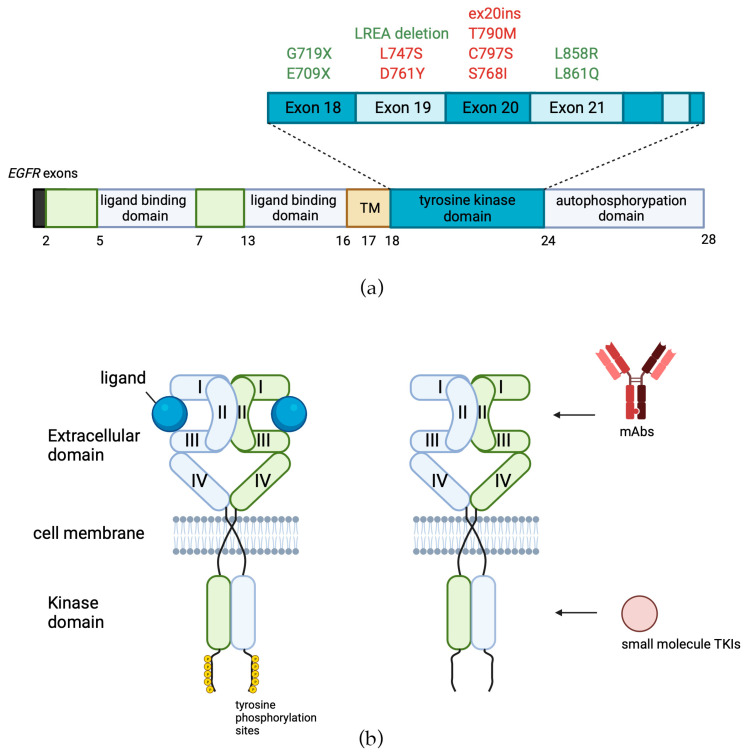
Figure 3.
(a) Structure of EGFR gene. EGFR exons 18–21 encode the tyrosine kinase domain and may contain mutations, playing a crucial role in the development and progression of different cancers with a strong proven relationship to resistance (red) and sensitivity (green) to specific TKIs. (b) Domain view of EGFR protein. Left, a schematic diagram of ligand-bound dimerized EGFR. Right, sites of inhibition of EGFR activity by different targeted drugs (mAb: monoclonal antibodies; TKIs: tyrosine kinase inhibitors). Created with BioRender.com (accessed on 18 October 2023).