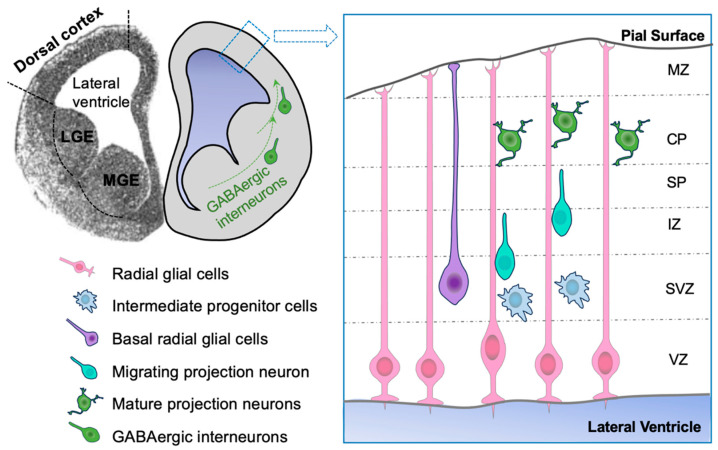
Figure 2.
The organization and cell types in the developing neocortex (adapted from Toresson et al. 1999). The ventricular zone (VZ) contains the cell body of radial glial cells (RGCs) that attach to the pia surface via the basal process, and to the lateral ventricle surface via the apical process. RGCs may directly generate neurons via asymmetric cell division, and the differentiated neurons migrate to the cortical plate along the RGC’s radial fibers. RGCs also generate multipolar intermediate neural progenitors (INPs) that divide in the subventricular zone (SVZ) to produce neurons. Basal radial glial cells (bRGCs) have a basal process attached to the pial surface, but no apical processes. bRGCs are more abundant in gyrified brains. In rodents, all GABAergic interneurons are generated in the ventral brain, and migrate tangentially to the dorsal cortex; glutamatergic projection neurons are generated in the dorsal brain and migrate radially to the cortical plate. VZ: ventricular zone; SVZ: subventricular zone; IZ: intermediate zone; SP: subplate; CP: cortical plate; MZ: marginal zone. LGE: lateral ganglionic eminence; MGE: medial ganglionic eminence.