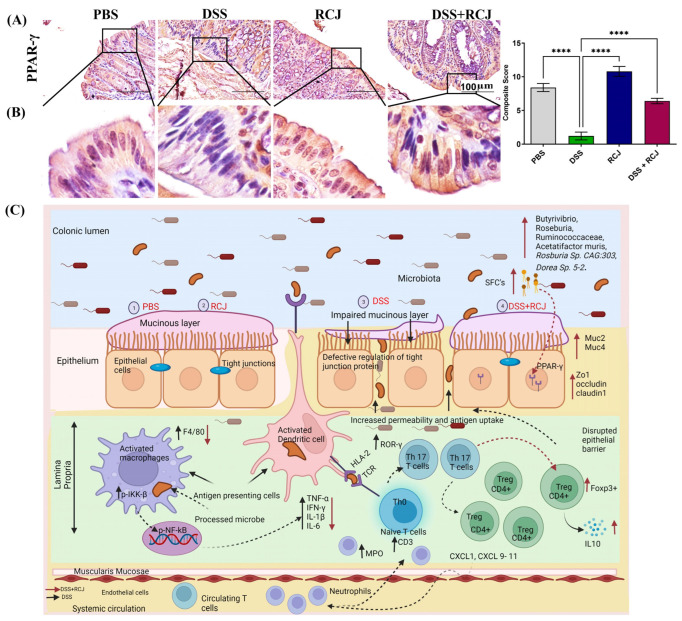
Figure 8.
(A) IHC staining for anti-inflammatory mediators PPAR-γ indicative of butyrate presence. Scale bars represent 100 µm for the IHC. Statistical significance was determined using one-way ANOVA, followed by the Tukey test. **** p ≤ 0.0001. (B) Zoom image of PPAR-γ expression. (C) Schematic model showing the mechanism by which RCJ alleviated DSS-induced colitis. Intestinal microbiota, oxidative stress, inflammation, and barrier integrity are all affected. RCJ treatment changed the gut microbiota by enriching bacteria such as Butyrivibrio, Roseburia, Ruminococcaceae, Acetatifactor muris, Rosburia Sp. CAG:303, Dorea Sp. 5-2, which subsequently led to increased production of SCFAs such as butyrate, which was evidenced by increased expression of PPAR-γ leading to a cascade of events, including anti-oxidative, anti-inflammatory, and barrier-protective responses. Ultimately, intestinal epithelial homeostasis is attenuated, and colitis is attenuated.