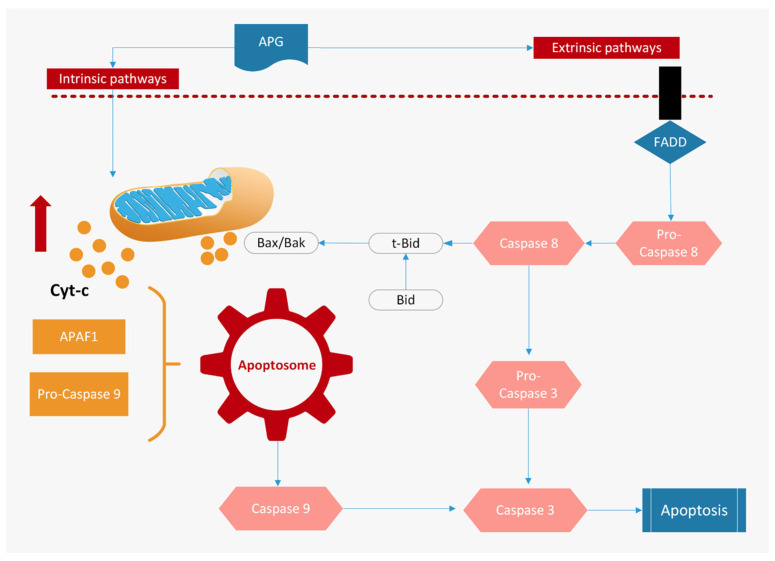
Figure 3.
Apigenin (APG) can modulate both intrinsic and extrinsic apoptotic pathways [1]. In the intrinsic pathway, apigenin changes mitochondrial membrane potential and causes the release of cytochrome C (cyt-C) in the cytoplasm, where it binds to Apaf-1 to form the apoptosome, which in turn activates caspase 9, initiating the caspase cascade. In the extrinsic pathway, apigenin upregulates the expression of Fas, TRAIL, and TNF-ligands, and of the adaptor proteins, such as FADD, which recruits caspase-8. Furthermore, apigenin modulates the expression of Bcl-2, Bax, STAT-3, and Akt proteins.