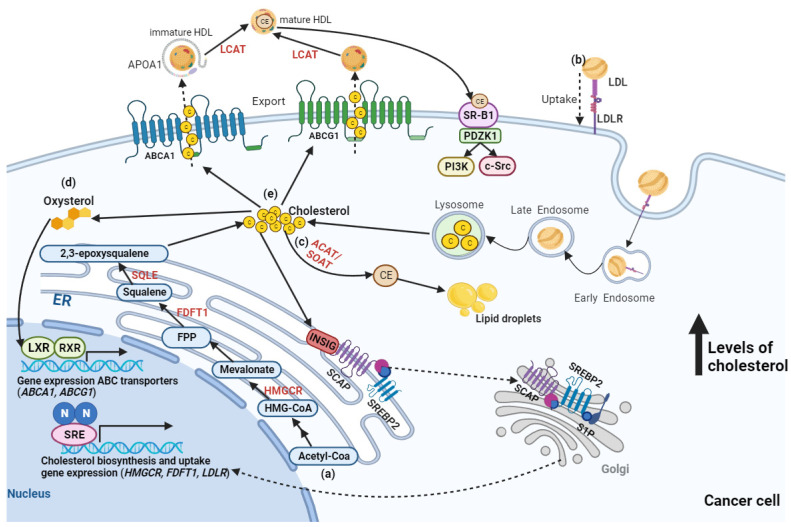
Figure 1.
Metabolism of cholesterol within an ovarian cancer cell. (a) De novo cholesterol biosynthesis starts with acetyl-coenzyme A (ACoA) and is then synthesized in more than 20 enzymatic steps, while 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase (HMGCR), farnesyl-diphosphate farnesyltransferase 1 (FDFT1), and squalene epoxidase (SQLE) act as rate-limiting enzymes. (b) Cholesterol uptake is mediated by the ligation of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) to its receptor (LDLR), which is followed by endocytosis of LDL. This uptake creates high cholesterol accumulation, leading to intracellular lipo-toxicity and suppressing sterol-regulatory element binding protein 2 (SREBP2) transcription factor activity, thereby restricting the expression of enzymes involved in cholesterol synthesis and LDLR-mediated cholesterol uptake. (c) Excess cholesterol is converted into cholesterol esters (CE) by acyl-CoA: cholesterol acyltransferase 1 (ACAT1), also known as sterol-O-Acyl transferase 1 (SOAT1) enzyme, is then stored in lipid droplets. (d) Excess cholesterol is also converted to oxysterol through multiple enzymatic or non-enzymatic processes, which then activates liver X receptor (LXR)-retinoid X receptor (RXR) signaling and results in gene expression of ATP-binding cassette (ABC) subfamily A member 1 (ABCA1) and ABC subfamily G member 1 (ABCG1), which promote the (e) cholesterol efflux pathway. The cholesterol exported by ABCA1 is transported by lipid-free apolipoprotein A-1 (APOA1), producing immature high-density lipoprotein (HDL) that is converted into mature HDL by lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase (LCAT) in the plasma. The cholesterol exported by ABCG1 can directly become mature HDL, which can be consumed by liver cells or steroidogenic cells (e.g., ovarian cells) by binding to HDL receptor-scavenger receptor type B1 (SR-B1), activating downstream pathways involved in cancer cell proliferation, growth, and migration. Figure created in BioRender.com (accessed on 24 November 2023). ER—Endoplasmic reticulum; FPP—Farnesyl pyrophosphate; INSIG—insulin-induced gene; PDZK1—PDZ Domain Containing 1; SCAP—SREBP-cleavage activating protein; S1P—site-1 protease; SRE—steroid response element.