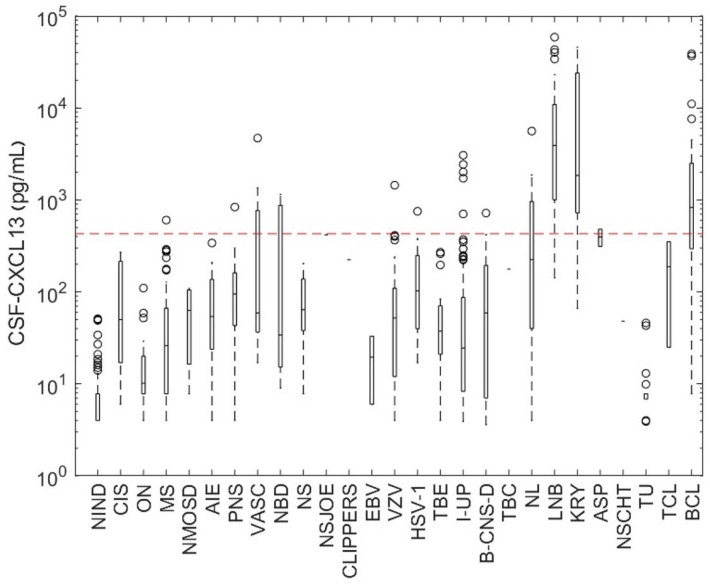
Figure 1.
CSF-CXCL13 in various neurological disorders. The selected patients from the Biobank are represented based on the level of CXCL13 and the respective disease. CXCL13 concentrations in the different neurological diseases are illustrated as boxplots. Their bars represent interquartile ranges (IQR; 25–75% percentile), horizontal lines indicate medians, dotted lines represent the upper and lower whiskers (+/−1.5 × IQR), and open circles represent outliers. The red dashed line represents a reference line for the CXCL13 cut-off of 428.92 pg/mL calculated with receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis to distinguish neuroborreliosis from other neuroinflammatory diseases with the highest sensitivity and specificity. NIND: non-inflammatory neurological diseases, CIS: clinically isolated syndrome, ON: optic neuritis, MS: multiple sclerosis, NMOSD: neuromyelitis optica spectrum disease, AIE: autoimmune (limbic) encephalitis, PNS: paraneoplastic syndrome, VASC: CNS-vasculitis, NBD: Neuro-Behçet’s disease, NS: neurosarcoidosis, NSJOE: Sjögren’s syndrome (neurological), CLIPPERS: chronic lymphocytic inflammation with pontine perivascular enhancement responsive to steroids, EBV: Epstein–Barr virus, VZV: varicella-zoster virus, HSV-1: herpes simplex virus-1, TBE: tick-borne meningoencephalitis, I-UP: neuroinfectious diseases of unknown pathogens, B-CNS-D: bacterial meningitis, TBC: tuberculosis, NL: neurosyphilis, LNB: Lyme neuroborreliosis, KRY: cryptococcosis, ASP: aspergillosis, NSCHT: neuroschistosomiasis, TU: tumor of the CNS, TCL: T-cell lymphoma, BCL: B-cell CNS-lymphoma.