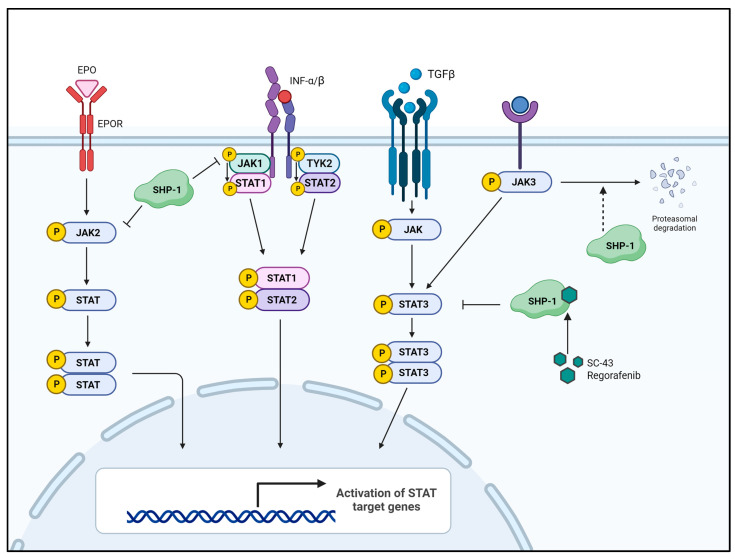
Figure 3.
SHP-1-mediated inhibition of the JAK/STAT signaling pathway. Several growth factors and cytokines activate their associated receptors, which, in turn, activate JAK. Activated JAK then activates STAT through phosphorylation and moves the activated STAT (p-STAT) to the nucleus, upregulating the expression of STAT-related genes. SHP-1 directly dephosphorylates STAT3 or its upstream JAKs, thereby inhibiting cell proliferation, survival, migration, and invasion. EPO—erythropoietin; EPOR—erythropoietin receptor; TYK2—tyrosine kinase 2.