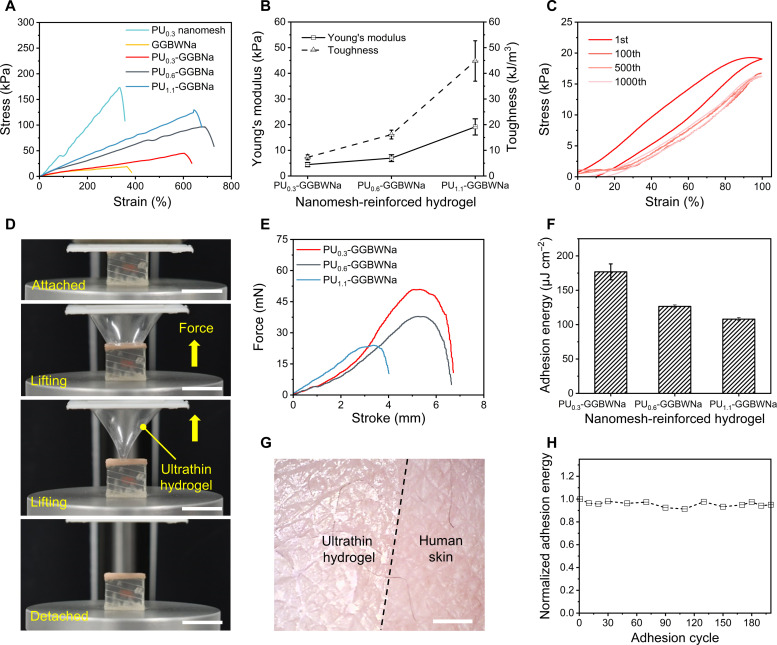
Fig. 3. Mechanical and adhesive characteristics of the PU nanomesh–reinforced hydrogels.
(A) Tensile stress curves of PU nanomeshes, hydrogels, and PU nanomesh–reinforced hydrogels. (B) Comparison of Young’s modulus and toughness of PU nanomesh–reinforced hydrogels calculated from (A). (C) Cyclic stretching/releasing curves of the ultrathin hydrogel under 100% strain. (D) Photographs demonstrating the separation process of the ultrathin hydrogel from artificial skin in a tack separation experiment. Scale bar, 1 cm. (E) Force stroke curves of PU nanomesh–reinforced hydrogels. (F) Comparison of the area adhesion energy and separation stroke for the PU nanomesh–reinforced hydrogels on artificial skin. (G) Microscope image of the ultrathin hydrogel seamlessly attached to the human skin. Scale bar, 1 cm. (H) Normalized adhesion energy of the ultrathin hydrogel during 200 attaching/detaching adhesion cycles. Error bars represent the SD of the measure values (n = 3).