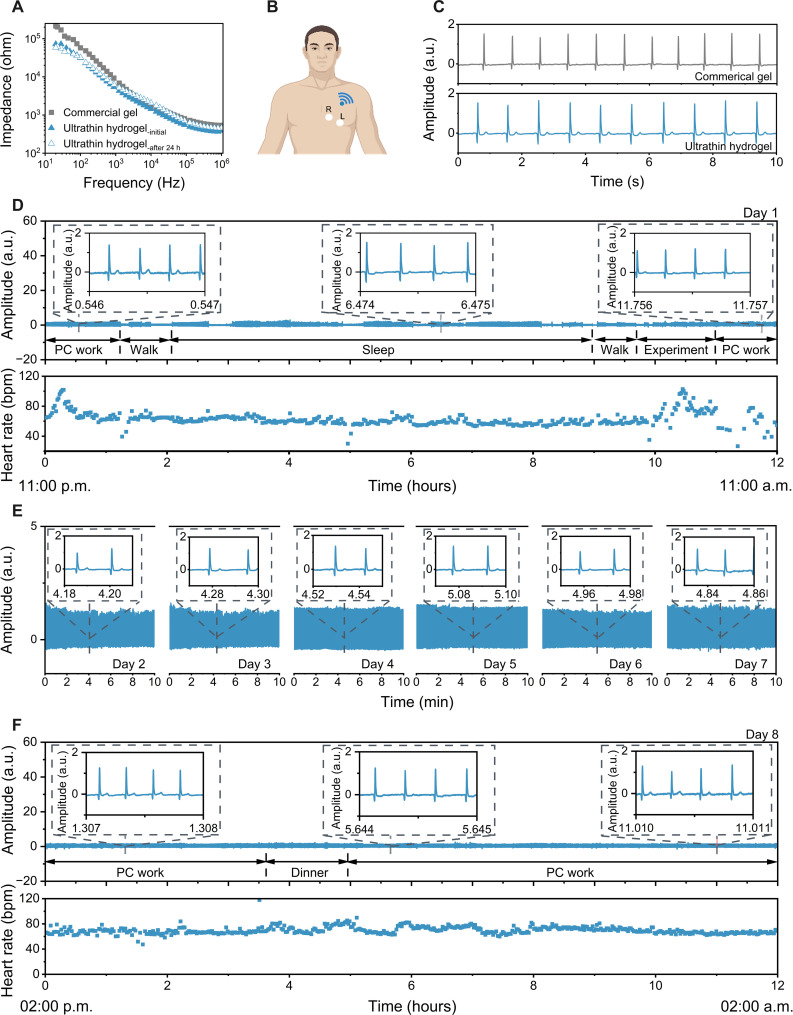
Fig. 4. Long-term, continuous high-fidelity ECG monitoring by the ultrathin hydrogels under daily life conditions.
(A) Skin-electrode contact impedance analysis of commercial gels and ultrathin hydrogels. (B) Schematic illustration of the experimental setup for wireless ECG measurement. (C) ECG signals recorded by commercial gels (top) and ultrathin hydrogels (bottom) in a sedentary state. (D) ECG signals monitoring (top) and the heart rate results (bottom) by the ultrathin hydrogels during various normal daily activities on day 1 from 11:00 a.m. to 11:00 p.m. The insets show the zoomed-in data segments. (E) ECG signals monitoring from day 2 to day 7, the insets show the zoomed-in data segments. (F) ECG signals monitoring (top) and the heart rate results (bottom) by the ultrathin hydrogels during various normal daily activities on day 8 from 2:00 p.m. to 2:00 a.m., respectively. a.u., arbitrary units; PC, personal computer.