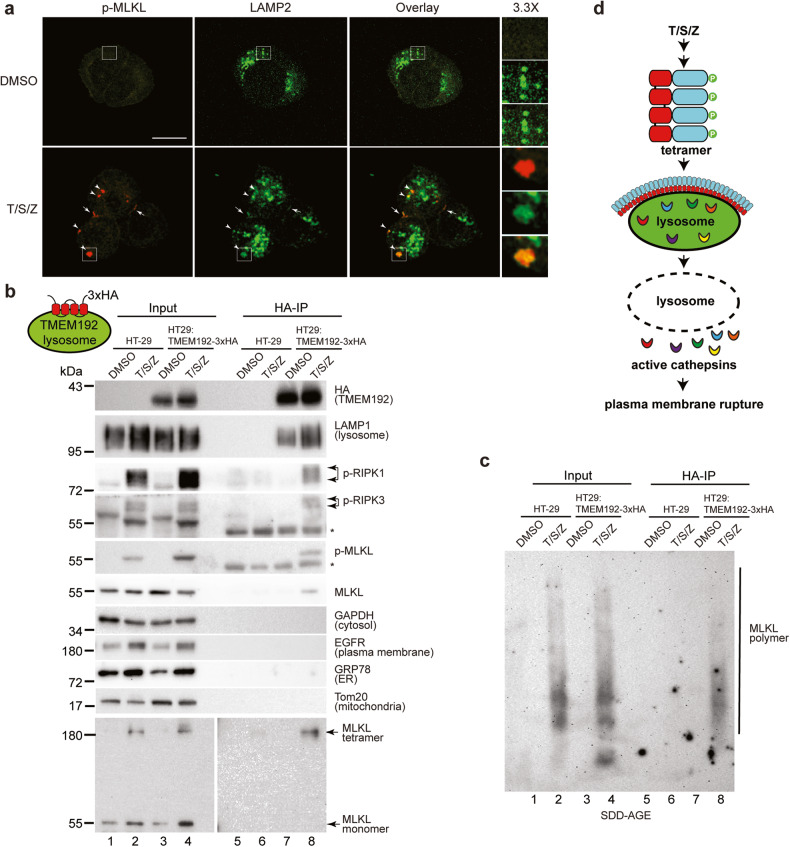
Fig. 2. Activated MLKL translocates to the lysosomal membrane after necroptotic induction.
a HT-29 cells were treated with DMSO or T/S/Z for 4 h, followed by staining with antibodies against p-MLKL and LAMP2. Arrowheads mark cytosolic puncta and arrows denote plasma membrane puncta. b Lysosomal membrane protein TMEM192 with 3×HA tags at C-terminus was stably expressed in HT-29 cells to establish HT-29:TMEM192-3xHA cell line. Cells were treated with DMSO or T/S/Z for 4 h and lysosomes were precipitated with anti-HA magnetic beads as described in methods. Western blotting was performed with the indicated antibodies. * denotes non-specific signals from the IgG heavy chain. For tetramer detection, non-reducing SDS-PAGE was performed. LAMP1, lysosome marker; GAPDH, cytosol marker; EGFR, plasma membrane marker; GRP78, ER marker; and Tom20, mitochondria marker. Antibodies against phospho-S166 of RIPK1 (p-RIPK1) and phospho-S227 of RIPK3 (p-RIPK3) were also used. c Immunoprecipitated lysosomes were subjected to semi-denaturing detergent agarose gel electrophoresis (SDD-AGE) and Western blotting was performed with an MLKL antibody. d Working model. Upon activation, MLKL translocates to the lysosome membrane, leading to LMP and release of active cathepsins into cytosol, and eventual plasma membrane rupture.