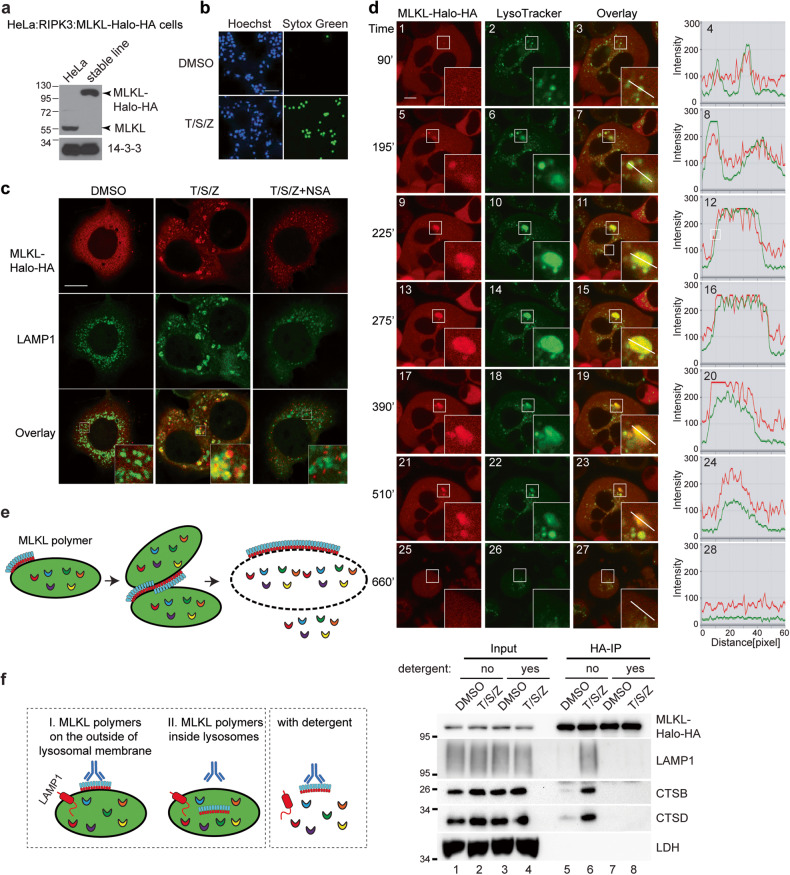
Fig. 3. Activated MLKL polymerizes on the lysosomal membrane to promote lysosome fusion and lysosomal membrane permeabilization.
a Characterization of the HeLa:RIPK3:MLKL-Halo-HA cell line. After CRISPR/Cas9-mediated knockout of endogenous MLKL in HeLa cells, MLKL fused with C-terminal Halo-Tag and HA-tag as well as FLAG-RIPK3 was engineered to stably express in these cells. Western blotting was performed with an MLKL antibody. b HeLa:RIPK3:MLKL-Halo-HA cells were treated with DMSO or T/S/Z overnight and then stained with Hoechst and a cell-impermeable DNA dye Sytox Green. Hoechst stains all cells and Sytox Green stains dead cells with compromised cell membranes. Scale bar, 100 μm. c Cells were treated with the indicated inducers for 4 h, and the fluorescent dye TMR was added to stain MLKL-Halo. Cells were then fixed and stained with an anti-LAMP1 antibody. Insets were shown at a 4 × magnification. Scale bar: 10 μm. d HeLa:RIPK3:MLKL-Halo-HA cells were stained with TMR for MLKL-Halo and LysoTracker Green DND-26 for lysosomes. Live cell imaging was recorded after T/S/Z treatment. Insets were shown at a 3 × magnification. A line intensity profile of the inset was analyzed with Zeiss software ZEN and shown on the right. Scale bar: 10 μm. e Working model. Upon activation, MLKL polymerizes on the lysosomal membrane, and MLKL polymers on different lysosomes further polymerize to promote lysosome clustering and fusion, eventually leading to LMP. f The left panel depicts a diagram illustrating the predicted outcomes of MLKL-Halo-HA-IP based on its localization, either outside or inside lysosomes. HeLa:RIPK3:MLKL-Halo-HA cells were treated with DMSO or T/S/Z for 4 h and harvested as described for lysosome-IP. MLKL-Halo-HA fusion protein was precipitated with anti-HA magnetic beads with or without 1% Triton X-100. Western blotting was performed with the indicated antibodies.