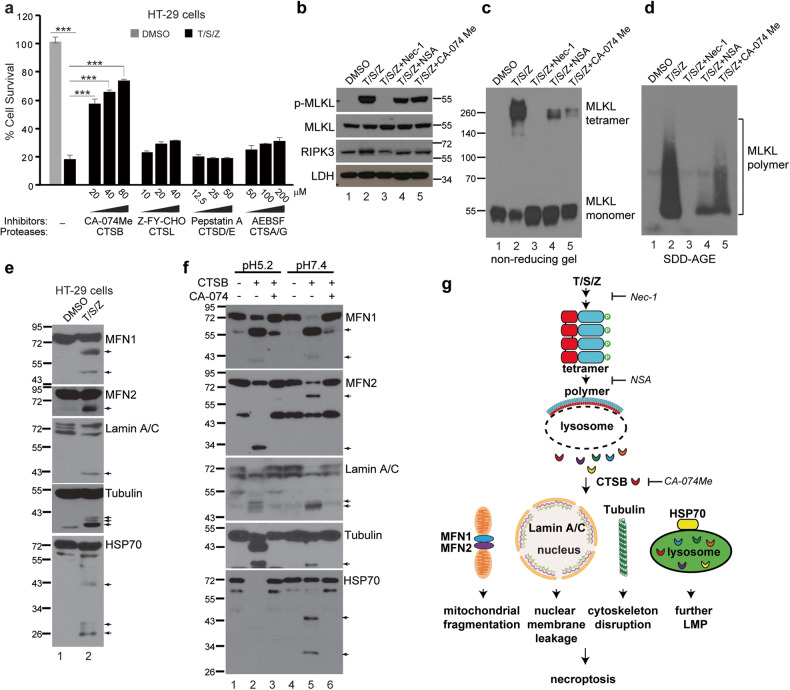
Fig. 4. Inhibition of lysosomal cysteine protease CTSB attenuates necroptosis and CTSB cleaves vital proteins at neutral pH.
a HT-29 cells were treated with DMSO or T/S/Z for 16 h in the presence of various concentrations of different protease inhibitors and cell survival was assayed by CellTiter-Glo. ***p < 0.001, mean ± SD are shown. b HT-29 cells were treated with the indicated inducers for 4 h and cell lysates were subjected to Western blotting with the indicated antibodies. 20 μM of CA-074Me, 10 μM of Nec-1 (RIPK1 inhibitor) and 5 μM of NSA (MLKL inhibitor) were used. Cell lysates were analyzed by non-reducing SDS-PAGE (c) or SDD-AGE (d) and probed with an MLKL antibody. e HT-29 cells were treated with DMSO or T/S/Z for 4 h and cell lysates were subjected to Western blotting with the indicated antibodies. Arrows denote the cleaved bands. f In vitro CTSB cleavage assay. Recombinant Tubulin or HSP70, or membrane fractions from HT-29 cells which were used as starting material for MFN1, MFN2, and Lamin A/C, were incubated with 100 ng of recombinant CTSB under conditions of pH5.2 or pH7.4, followed by Western blotting. CA-074 (20 μΜ) is a CTSB inhibitor. Arrows denote the cleaved bands. g Working model. Upon activation, MLKL tetramers form polymers on the lysosome membrane, leading to LMP and the release of active cathepsins into cytosol. Released CTSB cleaves MFN1, MFN2, Lamin A/C, Tubulin and HSP70 to promote mitochondrial fragmentation, nuclear membrane leakage, cytoskeleton disruption and further lysosome permeabilization, eventually resulting in cell death.