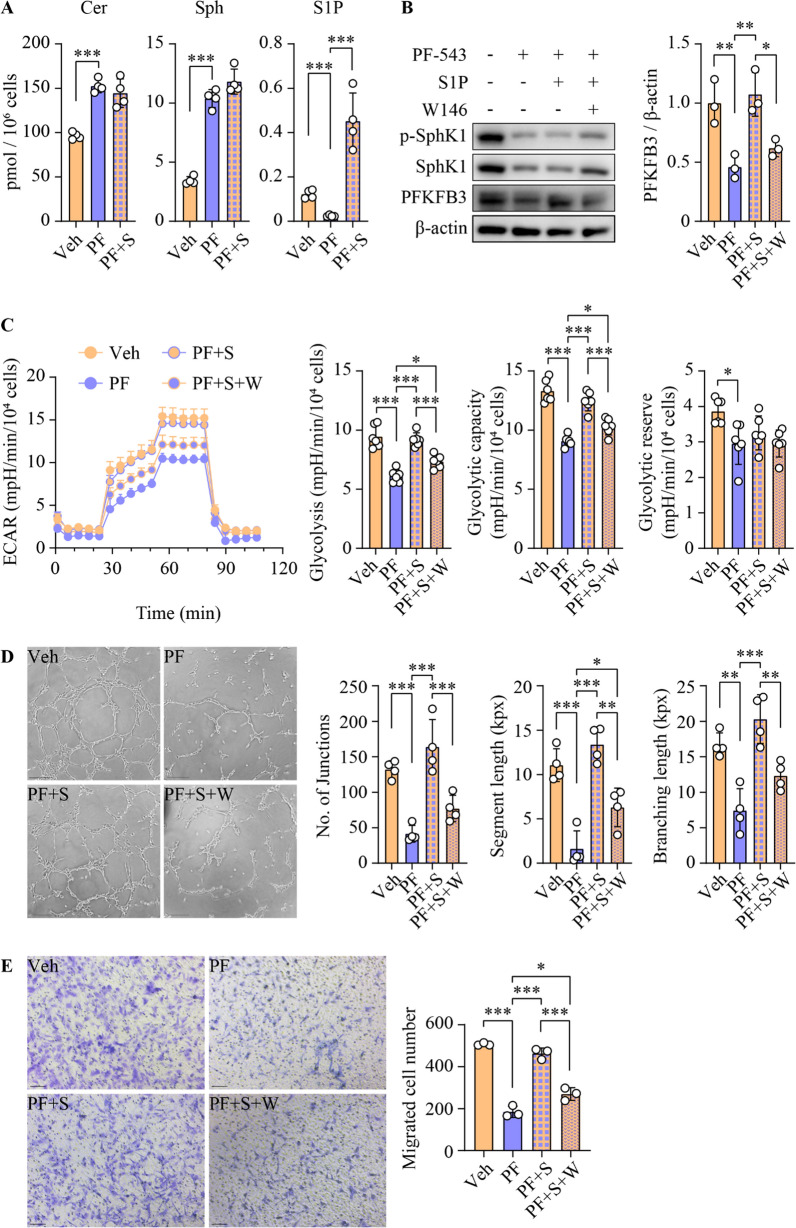
Fig. 6.
S1P is required for glycolysis and angiogenesis in an S1P1-dependent manner. Primary HUVECs were treated with 5 µM PF-543 (PF) and 0.5 µM S1P (S) for 16 h, with 2 µM S1P1 antagonist W146 added 1 h prior to these treatments. A Levels of ceramide (Cer), sphingosine (Sph) and S1P were analyzed using lipidomics; n = 4. B phospho(p)-SphK1, SphK1 and PFKFB3 protein levels were determined using Western blotting; n = 3. C Glycolytic rate, capacity and reserve were examined using Seahorse real-time glycolytic stress assay. ECAR, extracellular acidification rate; n = 6. D Tube formation was quantified as the number of junctions, segment length, and total branching length. kpx, 1000 pixels; scale bar = 200 μm; n = 4. E Cell migration was determined by transwell assay, and migrated cells were stained with crystal violet; scale bar = 100 μm; n = 3. Data are expressed as mean ± SD. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001