Figure 2. The SARS-CoV-2 S protein S1 subunit as an “arm” controlling the RBD down/up transition, a modulator of the propensity for pre- to postfusion conformation transition.
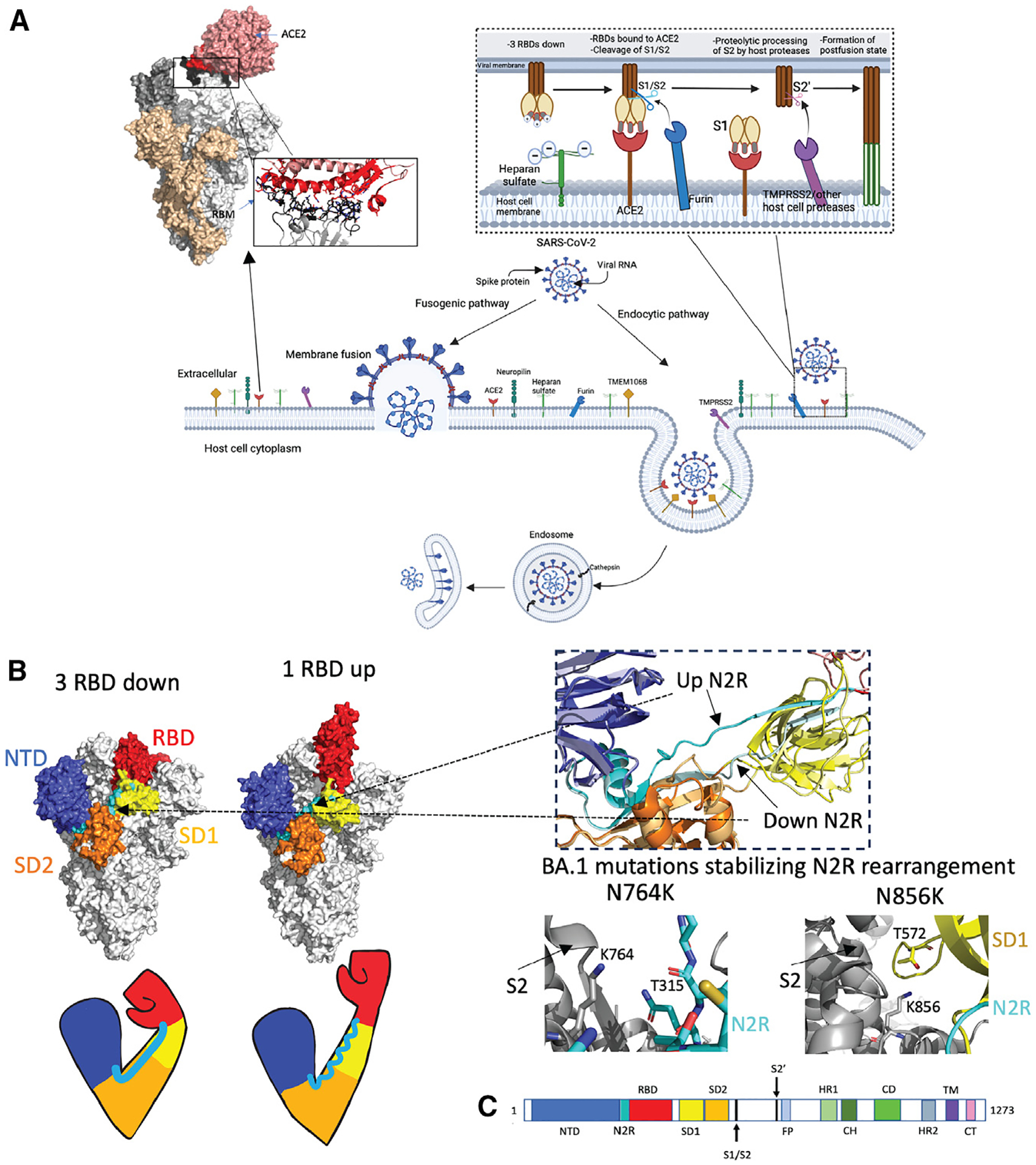
(A) Schematic representation of SARS-CoV-2 viral cell entry fusogenic and endocytic pathways. The top right inset shows interactions between SARS-CoV-2 S and heparan sulfate, ACE2, and proteases at the host cell surface, leading to the formation of the postfusion state. Top left: Omicron S bound to ACE2 (PDB: 7T9K) with a zoomed-in image of the receptor binding motif-ACE2 interaction. Interacting stretches in RBD 438–460 and 469–506 are colored black. Directly interacting residues in RBD: 444KVSGNY449, 453YRLF456, 473YQAGNK478, 484AGFNCYFPLRSYSFRPTYGVGHQ506: black sticks; ACE2 binding site (residues 18–56, 80–85, 325–333, and 347–360): red; Directly interacting residues on ACE2: 19STIEEQ24, 27TF28, 30DK31, 34HE35, 37ED38, 41YQ42, 45LA46, 48WN9, 52T, 55T, 80A, 82M, 83Y, 326G, 329EN330, 352GKGD FR357: red sticks. Figure made using BioRender.com and Pymol.
(B) Arm analogy of S protein S1 subunit. SARS-CoV-2 Omicron S in 3-RBD-down (left, PDB: 7TF8) and 1-RBD-up (right, PDB: 7TEI) conformations. NTD residues 24–293 (shoulder): blue; N2R residues 293–330: cyan; RBD residues 330–52813: red; SD1 (528–590): yellow; SD2 residues 590–680 (elbow): orange; S2: gray. Right top: zoom in on N2R region showing a comparison of the up RBD “rearranged” up N2R and the down N2R. Bottom right: BA.1 mutations N764K (PDB: 7TL9) and N856K (PDB: 7TF8), which stabilize the N2R rearrangement in Omicron BA.1 S.
(C) Schematic of the S sequence with visible S1 domains colored the same as in the above structure image. NTD, N-terminal domain; RBD, receptor-binding domain; SD1 and SD2, subdomains 1 and 2. The S2 subunit contains the fusion peptide (FP), heptad repeat 1 (HR1), central helix (CH), connector domain (CD), and HR2 subdomains. The transmembrane domain28 and cytoplasmic tail (CT) follow.
