Fig. 2.
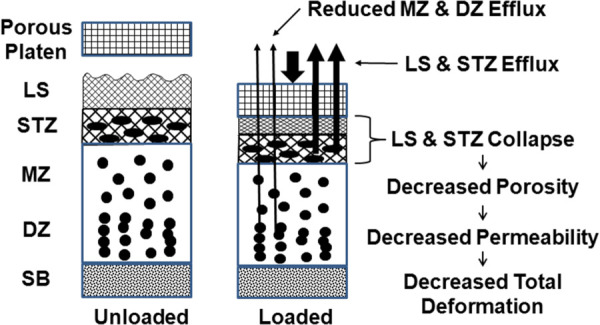
Schematic illustration of superficial zone (SZ) mechanical function. Loading the articular surface collapses the SZ (LS+STZ) as water is exuded, decreasing SZ porosity and permeability. This restricts interstitial fluid transport from the middle zone (DZ) and deep zone (DZ), thus decreasing extracellular matrix deformation.
