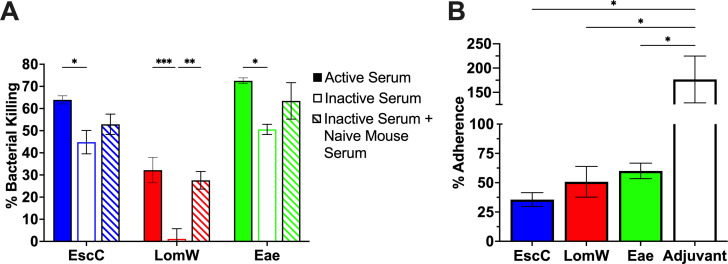
Fig 4.
Functionality and cross-reactivity of serum antibodies elicited by the AuNP vaccines. (A) To assess bactericidal properties of immune sera, C. rodentium DBS770 (1 × 105 CFU) was incubated with 10% active, inactive, or inactive plus exogenous complement sera. Bacterial killing was normalized using bacteria surviving after exposure to serum from adjuvant-only-treated mice. (B) For serum adherence inhibition, C. rodentium DBS770 (1 × 106 CFU) was incubated in the presence of inactivated sera from AuNP-EscC-, AuNP-LomW-, or AuNP-Eae-immunized mice, or from adjuvant-only or naïve mice. After incubation, bacteria were used to infect monolayers of Caco-2 cells (MOI 10) for 2 h. Percentages of adhered bacteria were determined with the following equation: output CFU/input CFU × 100. Percentages were normalized to the adherence of bacteria in the presence of naïve sera. Serum bactericidal and adherence inhibition data are expressed as means (±SEM) of results from at least 2 independent experiments using pooled sera from n = 12 mice. Significant differences in bacterial killing were determined via two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test and via one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparison’s test for bacterial adherence. *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, and ***P ≤ 0.001.