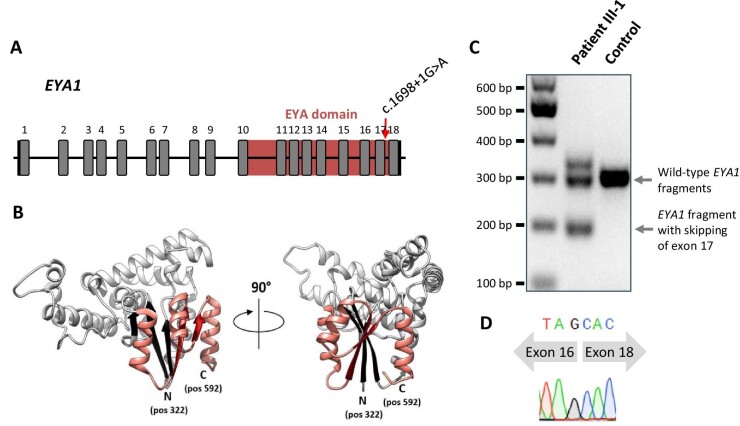
Figure 2:
Analysis of the EYA1 splice site affected by c.1698+1G>A. (A) Gene structure and location of canonical splice site mutation c.1698+1G>A in EYA1 (NM_000503.5) with transcription factor binding EYA domain formed by amino acids at positions 322–592. (B) Three-dimensional structure of EYA1 protein (PDB ID Q99502) with indicated N- and C-terminal ends of its EYA domain. The sequence preserved in the patients is depicted in light grey (including three strands from the beta sheet structure (black)), whereas the sequence part that is aberrant in the patients is shown in salmon (including two strands from the beta sheet structure (red)). (C) Agarose gel image, showing separation of mutant from wild-type EYA1 cDNA fragments. The analysis is based on a 290 bp amplicon spanning the cDNA region from the transcribed exon 16 through the 3′ untranslated region. The transcript corresponding to the lower band in the middle lane lacks exon 17. That corresponding to the upper band seems to lack exon 17, too, while also containing additional nucleotides, probably as an artifact from PCR. The cDNA was derived from primary dermal fibroblasts. (D) Chromatogram from Sanger sequencing the lower band evident in the middle lane in (C), showing the skip of exon 17.