Figure 1.
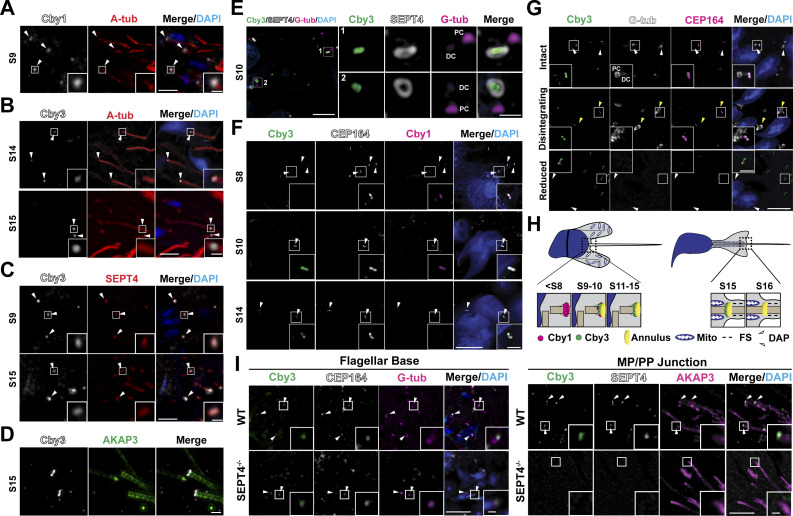
Localization of Cby1 and Cby3 during spermiogenesis. (A) Adult testis paraffin sections were immunostained for Cby1 (arrowheads) and A-tub. (B) Adult testis paraffin sections were immunostained for Cby3 (arrowheads) and A-tub. (C) Adult testis paraffin sections were immunostained for Cby3 (arrowheads) and SEPT4. (D) Adult testis frozen sections were immunostained for Cby3 and AKAP3. (E) Adult testis frozen sections were immunostained for Cby3, SEPT4, and G-tub. Note that G-tub prominently localizes to the proximal centriolar adjunct, which nucleates an aster of microtubules (Manandhar et al., 1998). (F) P30 testis frozen sections were immunostained for Cby1, Cby3, and CEP164. White arrowheads denote distal appendages. (G) Adult testis frozen sections were immunostained for Cby3, G-tub, and CEP164. The status of G-tub-positive centriolar structures is noted on the left. Yellow arrowheads indicate disintegrating G-tub-positive structures in the process of centrosome reduction. White arrowheads point to the base of flagella. (H) Model for Cby3 localization. Spermatogenic staging was assessed based on PNA lectin labeling of acrosomes and nuclear morphology. Mito, mitochondria; FS, fibrous sheath; DAP, distal appendage. (I) WT and SEPT4−/− adult testis paraffin sections were immunostained for Cby3, CEP164, and G-tub or Cby3, SEPT4, and AKAP3. Nuclei were detected with DAPI. Scale bars for A–C and G, 5 and 1 μm (insets); D, 1 μm; E and F, 10 and 1 μm (enlarged images or insets); I, 10 and 2 µm (insets).