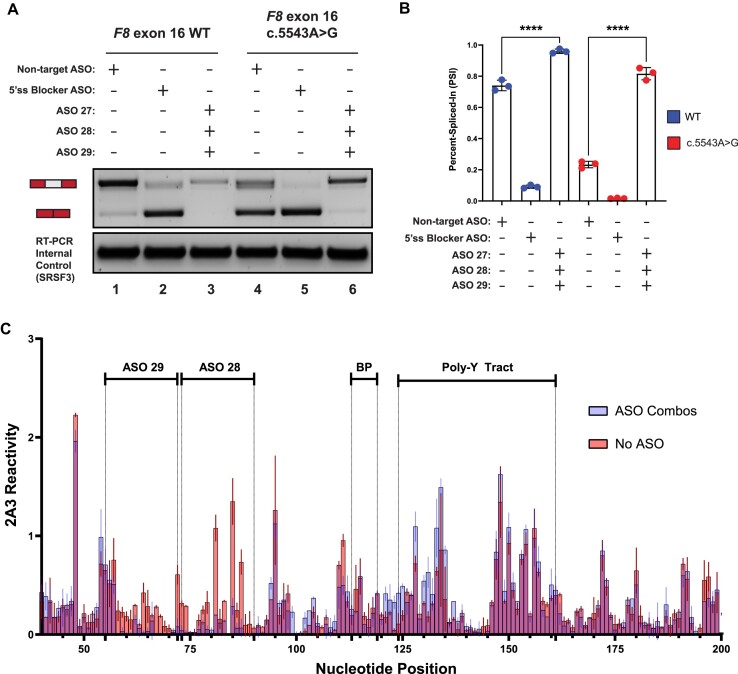
Figure 4.
A combination of ASOs targeting TWJ-3–15 can rescue splicing of the highly splicing-sensitive exon-16c.5543A>G variant by increasing 3′ss accessibility. (A) A representative agarose gel depicting the results from our in vitro cell-based splicing assays testing duo and trio ASO combinations’ ability to modulate reporter splicing (upper panel). The lower panel depicts an internal control corresponding to the SRSF3 mRNA (lower panel). Each splicing assay condition is annotated as shown in the matrix above the gel. Expected mRNA isoforms including or excluding the test exon are also annotated to the left of the agarose gel. (B) A plot quantifying the results from (A) using the PSI ratio. The WT context is annotated by a blue color whereas the exon-16c.5543A>G pathogenic variant is annotated by a red color. The same annotative matrix seen in (A) is used under the plot to label each ASO condition tested for each context. Statistical significance between comparisons are denoted by asterisks that represent P-values with the following range of significance: ns, P> 0.05, and ****P≤ 0.0001. Statistical significance was determined using analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Dunett’s post-hoc test. Each exon-16 splicing reporter context and condition tested contains three independent/biological replicates. (C) An overlay plot comparing normalized 2A3 reactivities between two distinct SHAPE probing conditions used to probe the exon-16c.5543A>G variant. One SHAPE condition probes exon-16c.5543A>G with ASOs present (annotated light blue), and the other condition probes exon-16c.5543A>G without ASOs present (annotated light red). Admixing of colors (indicated by purple hue) where this is indistinguishable overlap represents similar SHAPE reactivity values between the two probing conditions at that nucleotide position. The nucleotide positions where the ASOs bind, in addition to important splicing signals, are annotated in the plot. All SHAPE probing data presented were generated in vitro using the SHAPE reagent 2A3, and all subsequent data analysis was performed in RNA Framework. The sequence is numbered according to the nucleotide positions of the heterologous splicing reporter, from the 5′ to 3′ orientation.