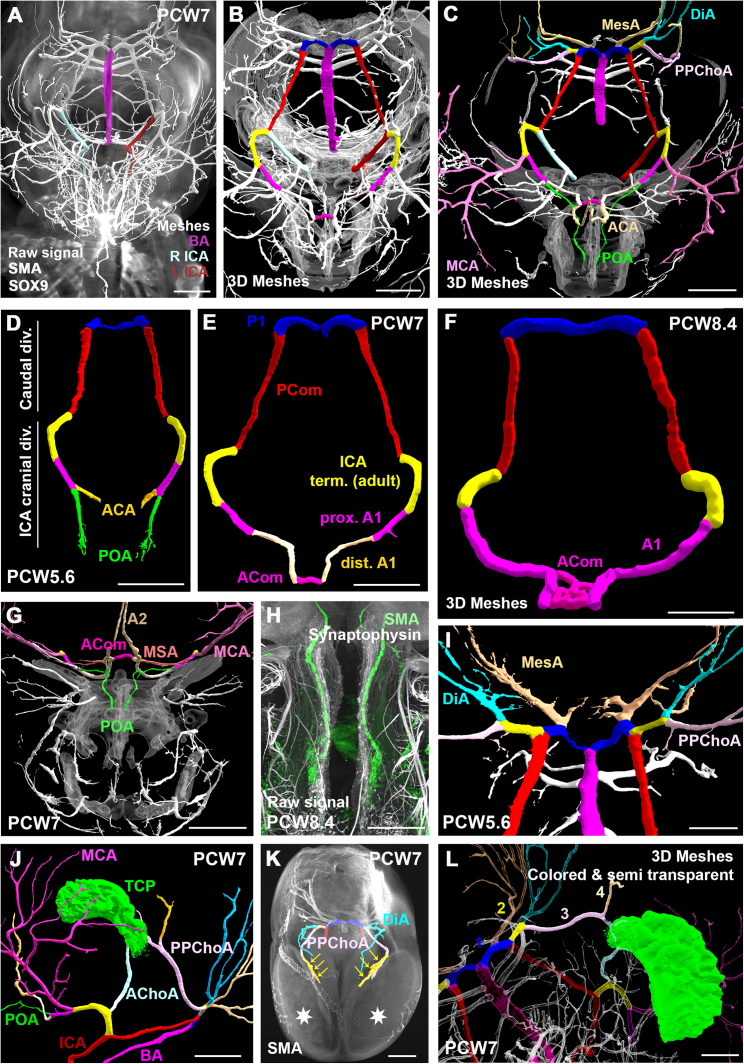
Figure 7.
Closure of the arterial circle of Willis and establishment of major cerebral arteries
Superior view of the circle of Willis in a PCW7 embryo (A–C and E).
(A) The circle is fed by the right and left internal carotid arteries (ICAs) and the basilar artery (BA).
(B and E) All segments of the circle of Willis are conspicuous including the caudal division of the ICA, subdivided into the most posterior P1 segment and posterior communicating (PCom) segment, the cranial division of the ICA with the adult ICA terminal segment, proximal A1 (distal to the origin of the middle cerebral artery (MCA) and proximal to the origin of the primitive olfactory artery (POA)), distal A1 and anterior communicating artery (ACom).
(C) Both MCA and post communicating anterior cerebral artery (ACA) are well identified. Posterior branches of the circle of Willis include the mesencephalic arteries (MesAs) as well as the primitive posterior choroidal arteries (PPChoAs) and diencephalic arteries (DiAs) arising from a common trunk (yellow).
(D–F) Anterior closure of the circle of Willis and subsequent growth in PCW5.6, PCW7, and PCW8.4 specimens. The series shows how the anterior cerebral artery first appears as a medial branch of the POA, before overshadowing the latter.
(G and H) The POA is shown to course into the nasal capsule along the olfactory filaments (H). Notice the medial striate arteries (MSAs) or recurrent arteries of Heubner arising from the peri-communicating segment of the ACA.
(I) The stem of the posterior cerebral artery (PCA) is represented by the most distal segment of the ICA caudal division (P1 segment). Notice the asymmetry of the P1 segments in the PCW5.6 embryo, showing early onset of a classical circle of Willis variant.
(J) The telencephalic choroid plexus (TCP) or choroid plexus of the lateral ventricule, is seen to be fed by both the anterior choroidal artery (AChoA) and the PPChoA.
(K) In another late PCW7 specimen, the PPChoAs give rise to prominent branches (yellow arrows) terminating at the medial posterior surface of the cerebral hemispheres (white stars).
(L) The adult posterior cerebral artery is a composite vessel combining the posterior segment of the ICA caudal division (1; blue), the diencephalic-choroid common trunk (2; yellow), the proximal stem of the primitive posterior choroidal artery (3; pink), and post choroidal branches (4; beige) that are shown to vascularize the posterior and medial surface of the developing telencephalic vesicles. The terminal choroidal branches are likely represented in the adult by the lateral posterior choroidal arteries.
Related to Figure S7.
Scale bars: 1 mm in (A)–(H), (J), and (K) and 500 μm in (I) and (L).