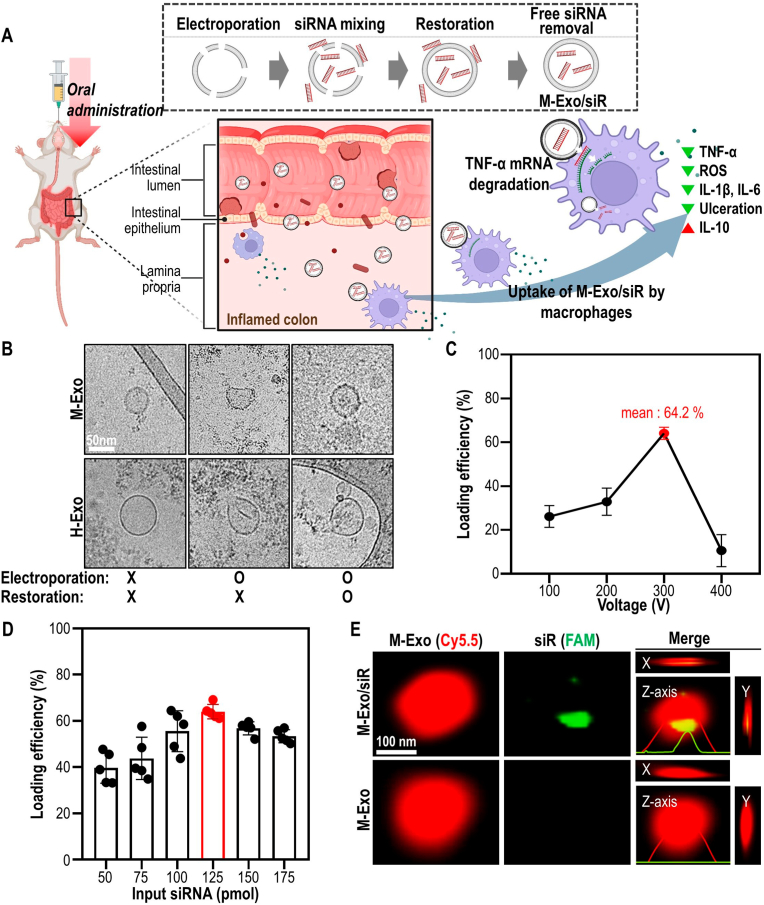
Fig. 1.
Preparation of M-Exo/siR and optimization of electroporation conditions for loading TNF-α siRNA into M-Exos. (A) Schematic of the colitis treatment process through oral administration of M-Exo/siR. (B) Comparative changes of morphology of exosomes according to electroporation conditions. (C) Loading efficiency of TNF-α siRNA into M-Exos according to voltage. The mixing ratio of M-Exos and siRNA is the same in all conditions. Data are mean ± SD (n = 9). (D) Loading efficiency according to the M-Exo and TNF-α ratio. The voltage, pulse number, and pulse length used for electroporation are consistent in all conditions. Data are mean ± SD (n = 5). (E) Representative SRM images were measured in the x-, y-, and z-axis directions of M-Exo/siR. Red (Cyanine 5.5-labeled M-Exos); Green (5′-Fluorescein phosphoramidite-labeled TNF-α siRNA).