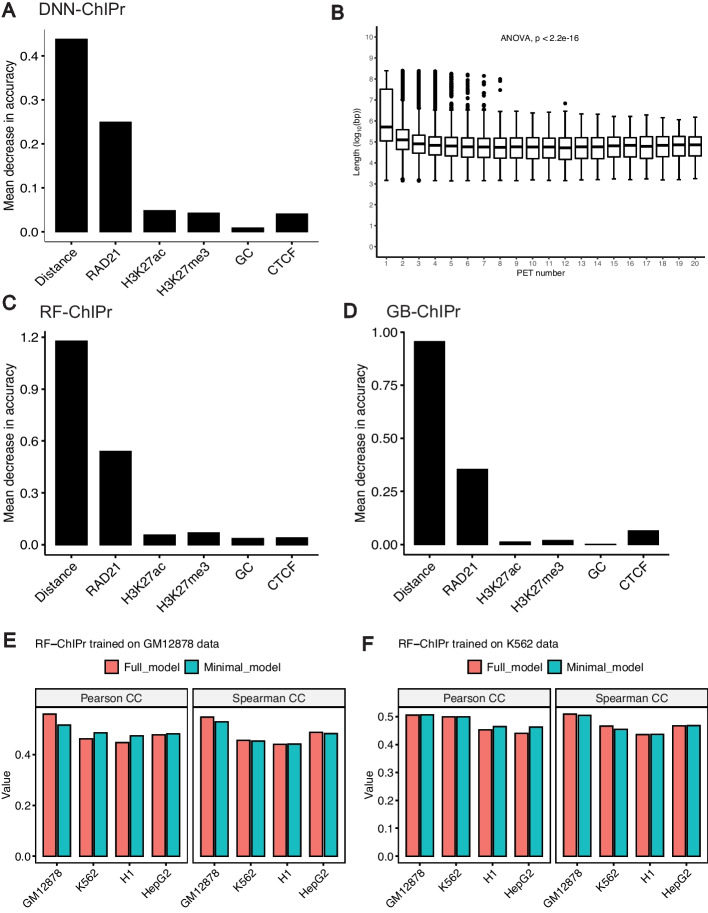
Fig. 7.
Contributions of input features to ChIPr outputs. A The drop in mean absolute error when comparing predicted interactions with the original ones when training DNN-ChIPr while removing one of the input features at each time. B The relation between the number of RAD21 interactions with different strengths and the genomic distance between the two interacting peaks. C, D The importance of the inputs features for RF-ChIPr (C) and GB-ChIPr (D) using the permutations test. E, F Comparison between the genome-level performance of RF-ChIPr minimal and full models trained on GM12878 data (E) and K562 data (F), respectively. The data is split into training data (75%) and test data (25%). In E, the performance of GM12878 is measured on the GM12878 test data. Similarly, in F, the performance of K562 is also measured on the K562 test data