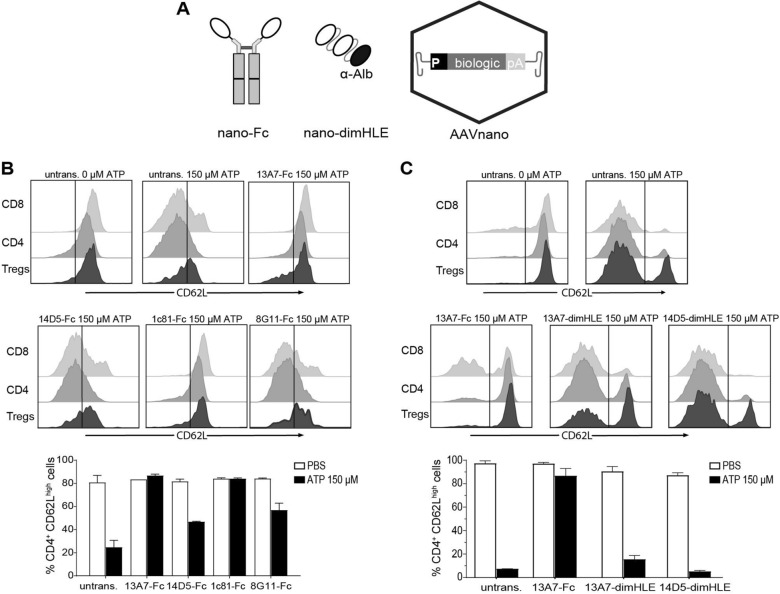
Fig. 1.
Comparison of different AAVnano vectors and their potential to modulate P2X7 function in vivo after i.m. administration. Mice (n = 3) were injected with Nb-encoding AAV vectors in the gastrocnemius muscles at day 0. A Scheme of the nanobody-based biologics used in our study and the AAVnano vectors coding for these constructs. Two formats were evaluated, a nanobody-Fc fusion protein, termed nano-Fc, where the Fc region of mouse IgG1 carries the “LSF” mutations T252L, T254S, T256F to confer increased half-life in vivo, or a nanobody dimer (dim) fused to a third anti-albumin (Alb8) nanobody, termed nano-dimHLE, that also confers half-life extension (HLE) in vivo. B, C AAVnano vectors coding for the indicated nanobody-based biologics were injected i.m. at a dose of 1011 vg/mouse. Control mice were not transduced with AAV (untransd.). Blood samples were collected 15 (B) or 17 (C) days post i.m. injections and the functional activity of P2X7 on the surface of T cell subsets was evaluated after incubation with 150 µM ATP. Flow cytometry profiles of CD62L expression and percentages of CD4+CD62Lhigh cells in the gated CD8+, CD4+CD25−, or CD4+CD25+ (Tregs) subsets are shown. One representative experiment out of at least two is shown with n = 3 mice per experiment