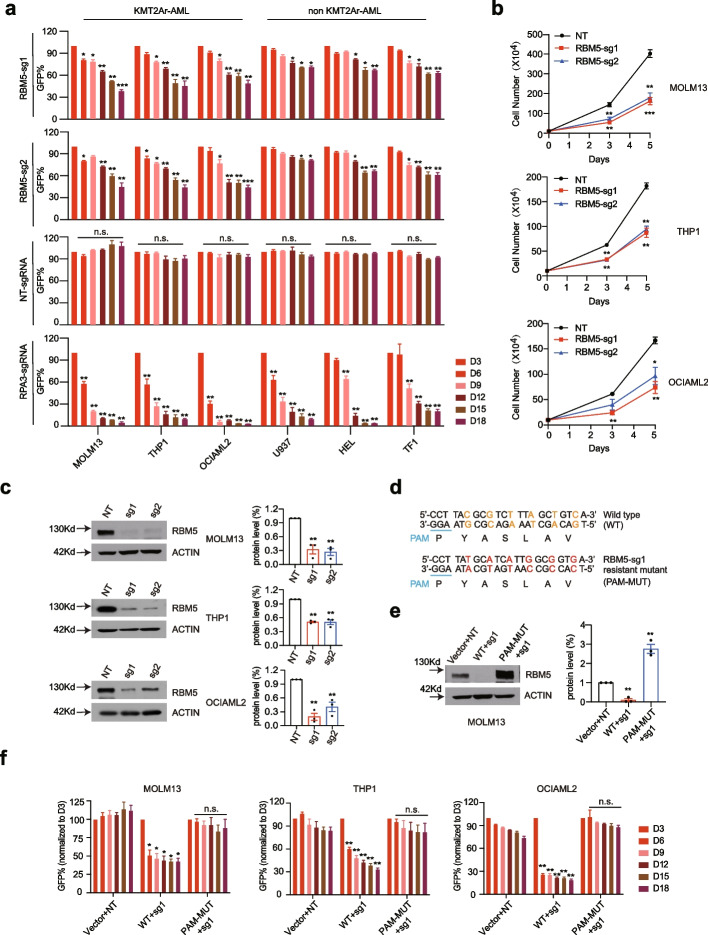
Fig. 2.
Disruption of RBM5 delays the growth of leukemia cells in vitro. a Competitive proliferation assay (CPA) was conducted in Cas9 stably expressed AML cells lines, including MOLM13, THP1, OCIAML2, U937, HEL, and TF1 after transduced with GFP reporter-based lentiviral sgRNAs (NT, RPA3, RBM5-sg1, RBM5-sg2) at about ~ 50% efficiency. The GFP% was quantified at days 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, and 18 by flow cytometry to evaluate the growth disadvantage. The guide RNA targeting the survival essential gene RPA3 was included as a positive control, and the guide RNA targeting the non-target (NT) gene was included as a negative control. Data shown are means ± SEM from three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, unpaired Student’s t-test. b The proliferation ability of AML cells was monitored by cell counting assay in MOLM13, THP1, and OCIAML2 with stably expressed Cas9 after transduced by two respective sgRNAs targeting RBM5 (RBM5-sg1, sg2) and one non-targeting sgRNA. The guide RNA targeting non-target gene (NT) was used as a negative control. Data shown are means ± SEM from three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, unpaired Student’s t-test. c Immunoblotting of RBM5 in RBM5 sgRNAs targeted cells. The bands were scanned and statistically analyzed. Data shown are means ± SEM from three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, unpaired Student’s t-test. The β-ACTIN was used as a reference. d Schematic diagram of the sgRNA-resistant cDNA mutagenesis. The 22 bp DNA sequence and corresponding amino acids close to the sgRNA PAM region (blue) in RBM5 wild-type (WT) and RBM5-sg1-resistant mutant (PAM-MUT) cDNA are shown with the non-sensed mutated nucleotides highlighted in different colors (red and orange). e Immunoblotting was conducted by infecting MOLM13 cells overexpressing ectopic Venus empty vector, RBM5-wild-type cDNA (WT), RBM5-sgRNA1-resistant mutant cDNA (PAM-MUT) with lentiviral-sgRNAs against non-target gene (NT), and RBM5 (RBM5-sg1), and the bands were scanned and statistically analyzed. Data shown are means ± SEM from three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, unpaired Student’s t-test. The β-ACTIN was used as a reference. f Competition-based proliferation assays comparing the impact of sgRNAs on MOLM13, THP1, and OCIAML2 cell fitness, in the context of co-transduction with Venus empty vector control, RBM5-wild-type cDNA (WT), RBM5-sgRNA1-resistant mutant cDNA (PAM-MUT) (all monitored by Venus reporter). Data shown are means ± SEM from three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, unpaired Student’s t-test