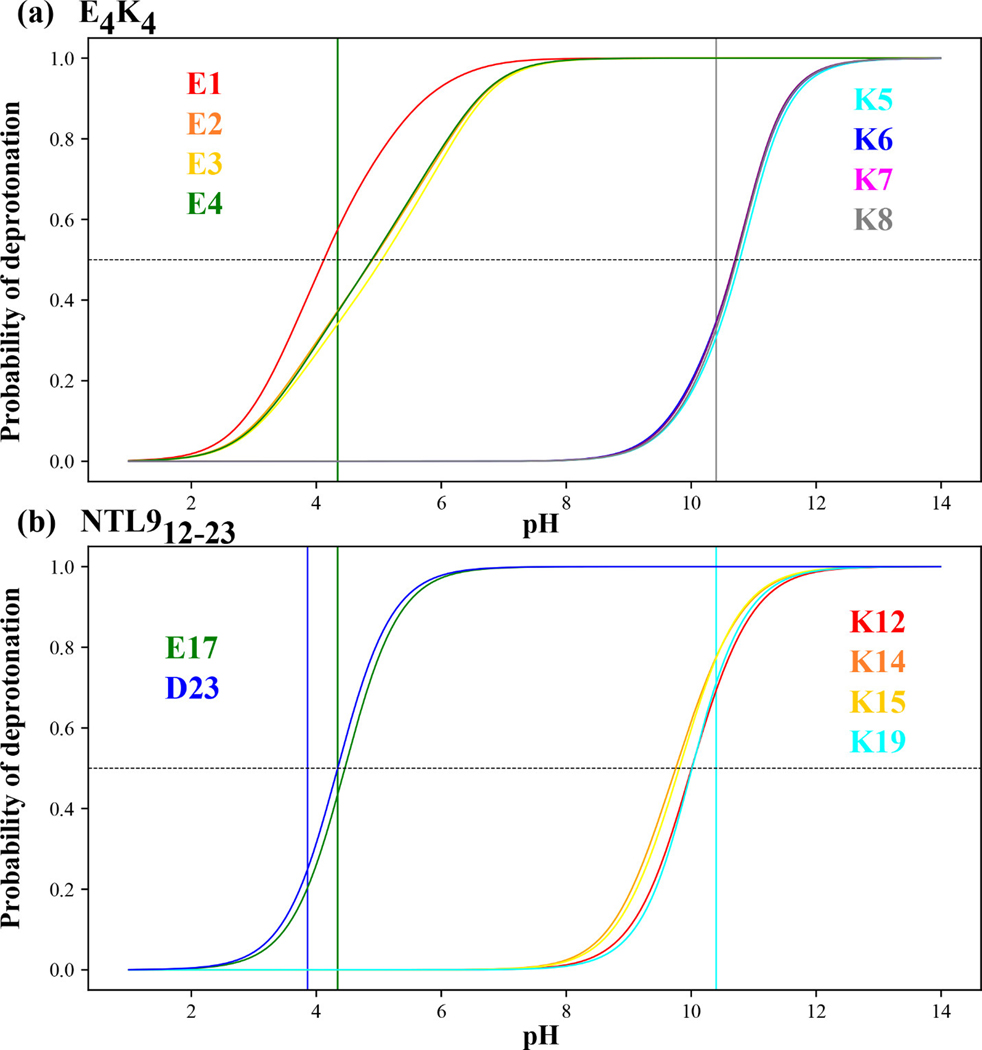
Figure 6: Probability of deprotonating ionizable residues as a function of pH.
(a) Results for the eight ionizable residues within . The green and black vertical lines intersect the abscissa at model compound values for Glu and Lys, respectively. The horizontal dashed line intersects the ordinate at the value of 0.5. The intersection of this horizontal dashed line with the residue-specific “titration curves” is used to estimate the apparent value for the residue in question. The curves are colored according to the residues as shown in the legend. (b) Results for the six ionizable residues within NTL912–23. The vertical lines shown in blue, green, and cyan intersect the abscissa at pH values that correspond to the model compound values for Asp, Glu, and Lys, respectively.