Fig. 1 |. Engineering strategy for programmable functional synthetic condensates.
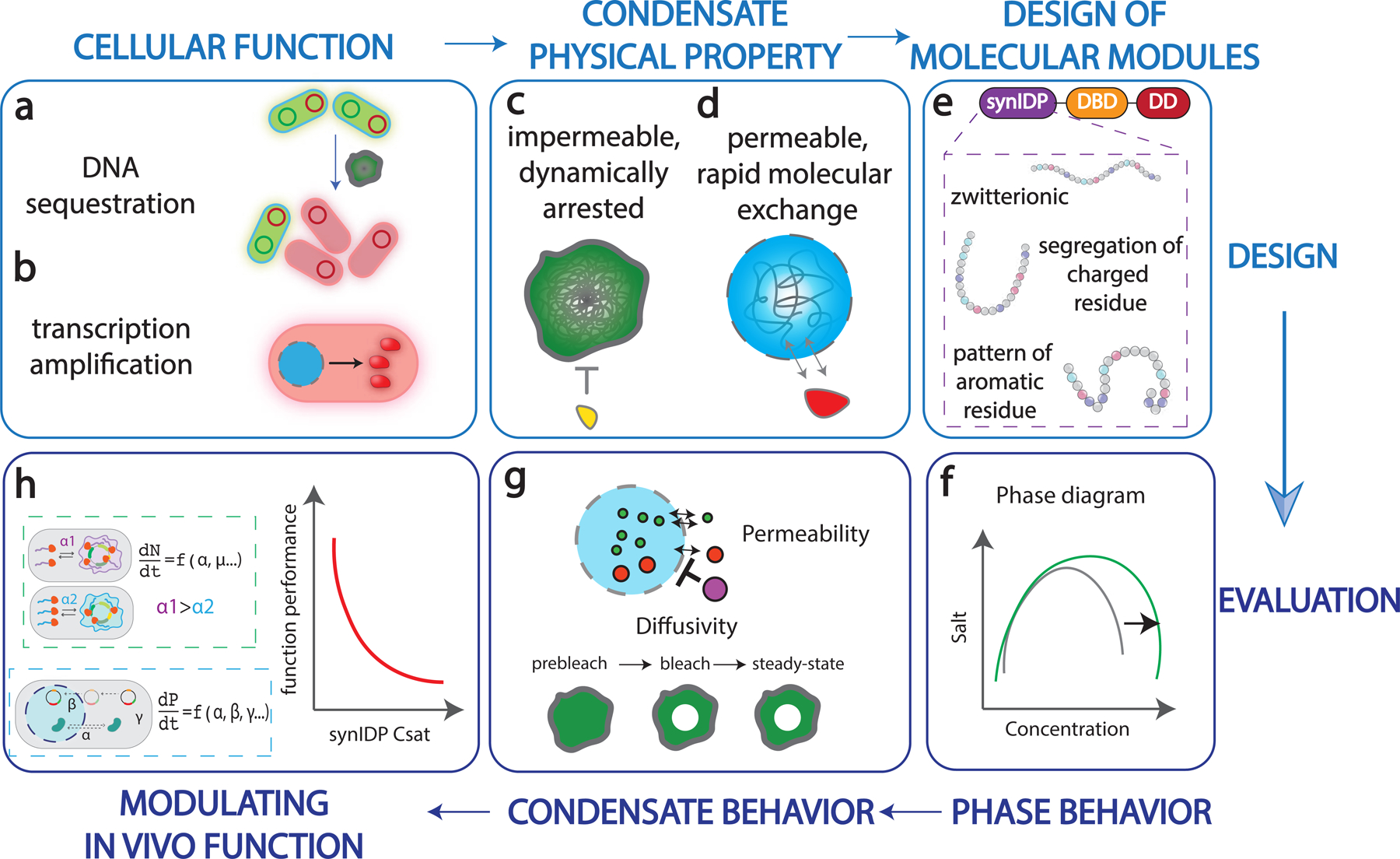
a, Condensate mediated DNA sequestration inhibits genetic materials (plasmid) from access of cellular machinery, inducing asymmetric plasmid partition.
b, Condensate mediated concentration of transcriptional machinery and target gene for transcription amplification.
c, A dynamically arrested and exclusionary condensate limits the exchange of molecules with the surrounding, thereby inhibiting a targeted functions in the cell.
d, A labile and inclusive condensate recruits and enriches key components, thereby amplifying a targeted function in the cell.
e, Design of modular protein components for the construction of synthetic condensate. The figure also summarizes characteristics of synthetic IDPs that affect different condensate properties.
f, Establishing the phase diagram based on different synIDPs and combinations of functional domains.
g, Evaluating functionally critical physical properties of synthetic condensates, including macromolecular permeability and diffusivity.
h, Computationally modeling the effects of different types of synthetic condensates on regulating cellular functions.
