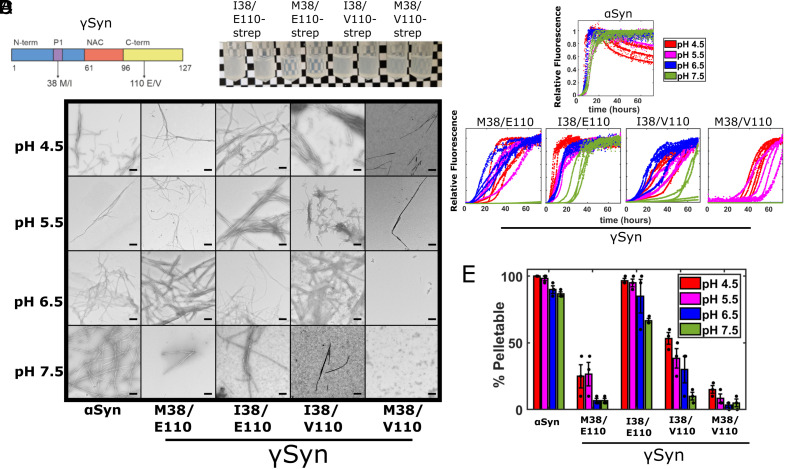
Fig. 2.
γSyn I38 variants result in more efficient amyloid fibril assembly. (A) Schematic showing the γSyn protein split into the N-terminal, NAC, and C-terminal regions highlighting the location of the two residues of interest. The previously discovered (50, 51) Glu/Val polymorphism at residue 110 in the C-terminal region (yellow) and the Met38Ile substitution in the P1 region (purple) within the N-terminal region (blue) are highlighted. Neither site is located within the NAC region (orange). (B) In-tube aggregation assay using 70 µM Strep-tagged γSyn variants. Images of tubes after 13 d of incubation at 37 °C in pH 8 buffer are shown. Variants containing the Ile38 are visibly more turbid, although some turbidity is observed for M38/V110. (C) ThT fluorescence of 80 μM αSyn and different γSyn variants monitored at 37 °C in 96-well plates. Assays were performed in a mixture of Tris and sodium acetate buffers at a total 20 mM ionic strength at pH 4.5 (red), 5.5 (pink), 6.5 (blue), or 7.5 (green). Four replicates of each are shown. Note that curves are normalized to a value of 1 if they reached a plateau, irrespective of the aggregate yield. Lag time and T50 values are shown in SI Appendix, Table S1. (D) Negative stain TEM images of samples at the end point of the ThT reactions. (Scale bar, 200 nm.) (E) Differential pelleting assay demonstrating the relative amount of protein that was found in the pellet after centrifugation at 100,000g for 30 min. The mean ± SD is shown (see also SI Appendix, Table S1).