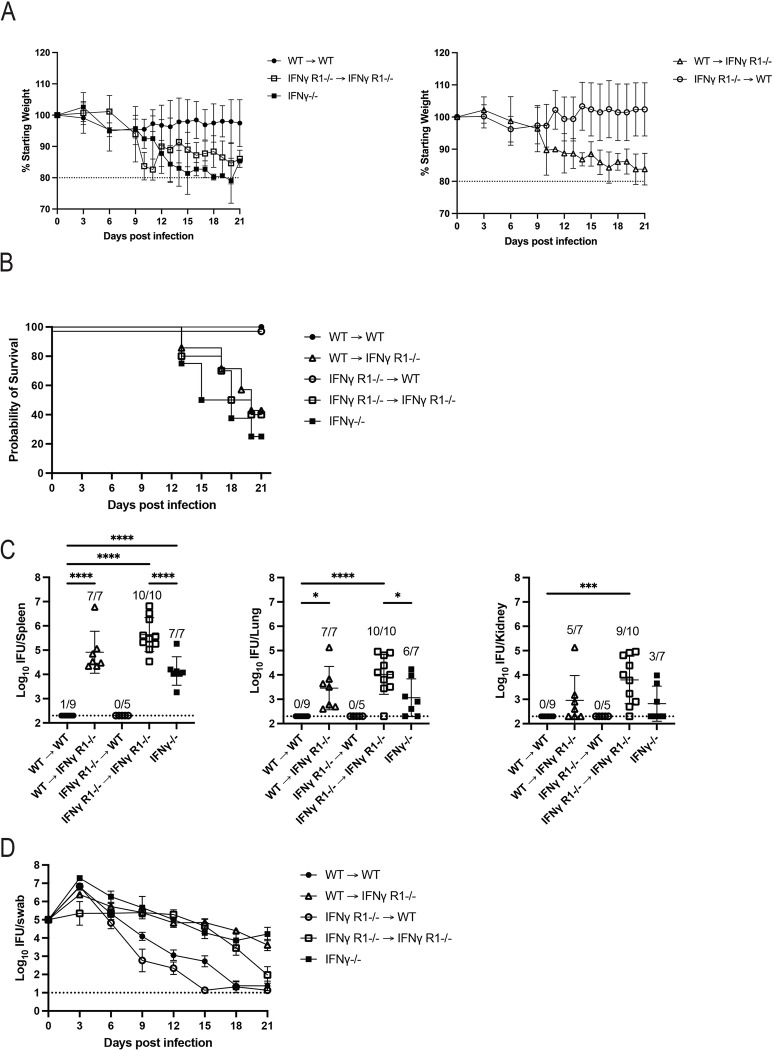
Fig 7. Bone marrow chimera mice require expression of IFN-γ receptor by the recipient host tissues, but not donor bone marrow cells to control systemic Chlamydia infection.
Four groups of bone marrow chimera mice were generated as follows: CD45.1 wild-type bone marrow was transferred into CD45.2 wild-type recipients (WT→WT), CD45.1 wild-type bone marrow was transferred into CD45.2 IFNγR1-/- recipients (WT→IFNγ R1-/-), CD45.2 IFNγR1-/- bone marrow was transferred into CD45.1 wild-type recipients (IFNγ R1-/-→WT), and CD45.2 IFNγR1-/- bone marrow was transferred into CD45.2 IFNγR1-/- recipients (IFNγ R1-/-→IFNγ R1-/-). These groups were synchronized and infected alongside an additional, unmanipulated group of IFNγ-/- mice. The weight of each mouse was monitored over the course of the experiment and mice were euthanized before day 21 post infection if their weight was below 80% of the starting value or their condition otherwise became too severe. All remaining mice were euthanized at day 21. Upon euthanasia, spleen, lung, and kidneys were harvested for counting Chlamydia burdens. (A) Graphs show the percentage of starting weight of each mouse over time ± SD. Controls and experimental groups are shown in separate plots for readability. WT→WT versus IFNγ R1-/-→WT is not significantly different. For WT→WT versus WT→IFNγ R1-/-, p<0.05 on days 11 and 14–20. For WT→WT versus IFNγ R1-/-→IFNγ R1-/-, p<0.05 on days 6, 10–11, and 16–21. For WT→WT versus IFNγ-/-, p<0.05 on days 12–19 and 21. For WT→IFNγ R1-/- versus IFNγ R1-/-→WT, p<0.05 on days 11, 14, 17, and 20–21 (mixed-effects analysis). (B) Survival curve. With Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons, WT→WT versus IFNγ R1-/-→WT is not significantly different while all other groups compared to WT→WT are significant. (C) Bacterial load measured in each organ at the time of euthanasia ± SD (1-way ANOVA). (D) IFUs isolated from vaginal swabs over the course of infection ± SEM. For WT→WT versus IFNγ R1-/-→WT, p<0.05 on day 15. For WT→WT versus WT→IFNγ R1-/-, p<0.05 on days 9–21. For WT→WT versus IFNγ R1-/-→IFNγ R1-/-, p<0.05 on days 9–18. For WT→WT versus IFNγ-/-, p<0.05 on days 12–21 (mixed-effects analysis). Data is combined from two experiments, total n are 9 for WT→WT, 7 for WT→IFNγ R1-/-, 5 for IFNγ R1-/-→WT, 10 for IFNγ R1-/-→IFNγ R1-/-, and 8 for IFNγ-/-.