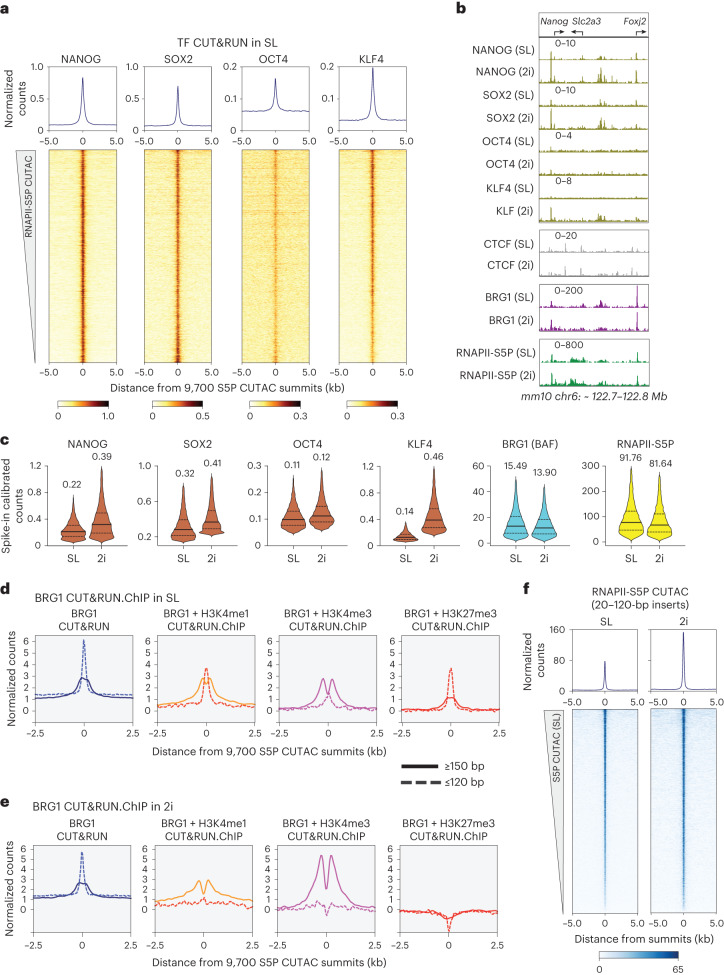
Fig. 5. Upregulation of pluripotency TFs results in enhanced nucleosome eviction.
a, Heatmaps (bottom) and average plots (top) of pluripotency TF CUT&RUN reads relative to RNAPII-S5P CUTAC summits, showing TF binding at sites of DNA accessibility. Heatmaps were sorted by decreasing accessibility (CUTAC signal). b, Representative genomic tracks comparing occupancy of TFs (CUT&RUN), BRG1 (CUT&Tag) and RNAPII-S5P (CUT&Tag) in SL and 2i conditions. All datasets were spike-in calibrated. c, Violin plots of spike-in calibrated CUT&RUN (TF) and CUT&Tag (BRG1 and RNAPII-S5P) signal distribution comparing factor occupancy over RNAPII-S5P CUTAC peaks in 2i versus SL. Median values (solid lines), upper and lower quartiles (broken lines) and outliers were calculated using the Tukey method; n = 9,700. Numbers on top are mean values. d,e, Enrichment of nucleosomal (≥150-bp, solid lines) and subnucleosomal (≤120-bp, broken lines) reads from BRG1 CUT&RUN and CUT&RUN.ChIP experiments, relative to S5P CUTAC summits, in SL (d) and 2i (e). f, Heatmaps (bottom) and average plots (top) of RNAPII-S5P CUTAC (20–120-bp reads only) relative to S5P CUTAC summits, comparing chromatin accessibility in 2i versus SL. All datasets are representative of at least two biological replicates.