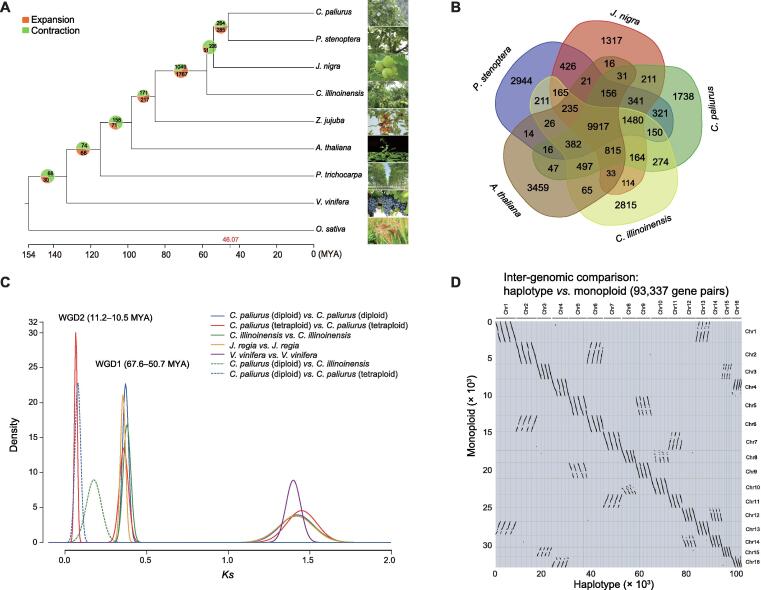
Figure 2.
Phylogenetic and comparative analyses of C. paliurus
A. Phylogenetic relationship of C. paliurus, C. illinoinensis, J. nigra, P. stenoptera, A. thaliana, Z. jujuba, V. vinifera, P. trichocarpa, and O. sativa. The divergence time among different plant species is labeled at the bottom. B. Venn diagram of orthologous and species-specific gene families in different plant genomes. C. Evolutionary analysis of the diploid and tetraploid C. paliurus genomes with the distribution of Ks values of orthologs.D. Synteny analysis between PA-tetra and PA-dip genomes. “monoploid” indicates a reference genome assembly with only one representative haplotype retained, whereas “haplotype” indicates fully phased genome with all the four haplotypes. C. illinoinensis, Carya illinoinensis; J. nigra, Juglans nigra; P. stenoptera, Pterocarya stenoptera; A. thaliana, Arabidopsis thaliana; Z. jujuba, Ziziphus jujuba; P. trichocarpa, Populus trichocarpa; O. sativa, Oryza sativa; Ks, synonymous substitution rate; MYA, million years ago.