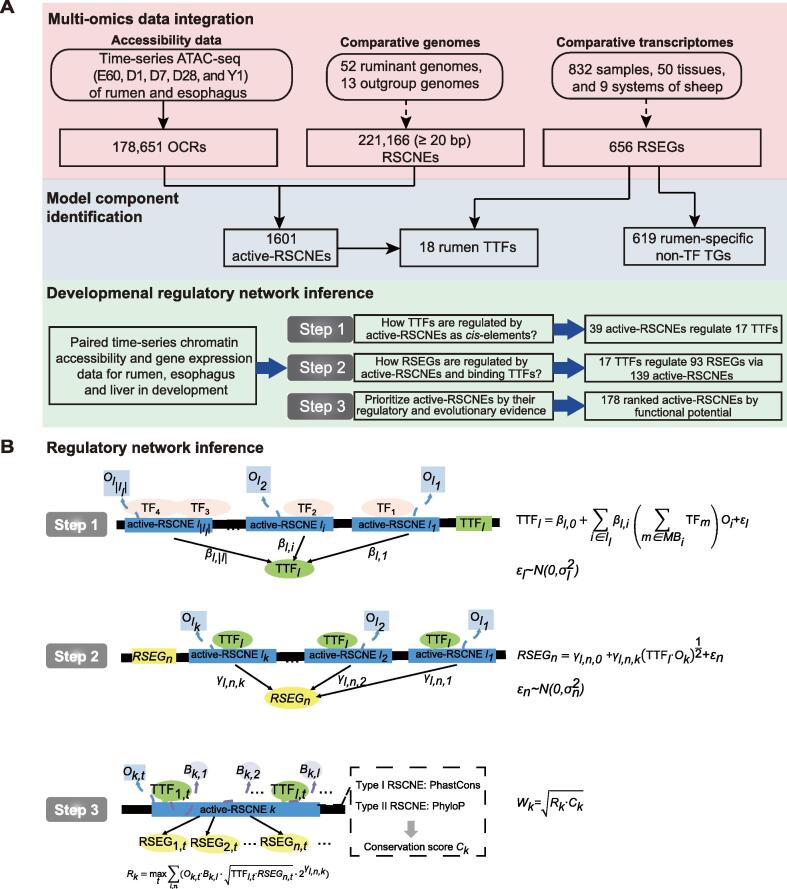
Figure 3.
CNEReg interprets RSCNEs by reconstructing the developmental regulatory network
A. CNEReg inputs paired time-series gene expression and chromatin accessibility data, ruminant comparative genomes, and comparative transcriptomes, and outputs the developmental regulatory network of active-RSCNEs. Three major steps of CNEReg include multi-omics data integration, model component identification, and developmental regulatory network inference. B. The developmental regulatory network reconstruction is further illustrated in three steps. Step 1: inferring the upstream regulation of rumen TTFs. Step 2: inferring the downstream regulation of TTFs to TGs via active-RSCNEs. Step 3: deriving active-RSCNE’s functional influence score by integrating regulatory strength in the network and evolutionary conservation score. The model components and notations of CNEReg are detailed in Table 1. TG, target gene; TF, transcription factor; TTF, toolkit transcription factor; CNEReg, conserved non-coding element interpretation method to integrate multi-omics data into gene regulatory network; RSCNE, ruminant-specific conserved non-coding element.