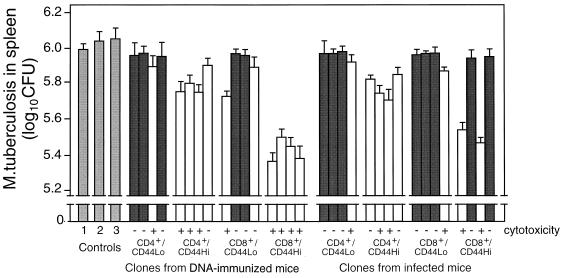
FIG. 7.
Protection by T-cell clones. Four strongly growing hsp65-responsive clones of CD4+/CD44lo and four of CD4+/CD44hi, four of CD8+/CD44lo, and four of CD8+/CD44hi phenotypes were selected from spleens of M. tuberculosis-infected and from hsp65 DNA-immunized mice. After characterization for hsp65 antigen-dependent cytotoxicity and IL-4 and IFN-γ production, they were tested for the ability to protect naive mice from challenge with M. tuberculosis as described in the legend to Fig. 5. The numbers of live bacteria in spleens 4 weeks after challenge are shown as mean log10 ± SD for groups of five animals. Dark-shaded and unshaded bars represent data from clones that produced IL-4 and IFN-γ, respectively. Controls were as follows: 1, untreated; 2 and 3, reconstituted, respectively, with CD4+/CD8− and CD8+/CD4− clones having irrelevant antigenic specificity.