Figure 4. Combinatorial targeting of MCL-1 and microtubules causes synergistic cytotoxicity that correlates with mitotic arrest independent of apoptosis induction.
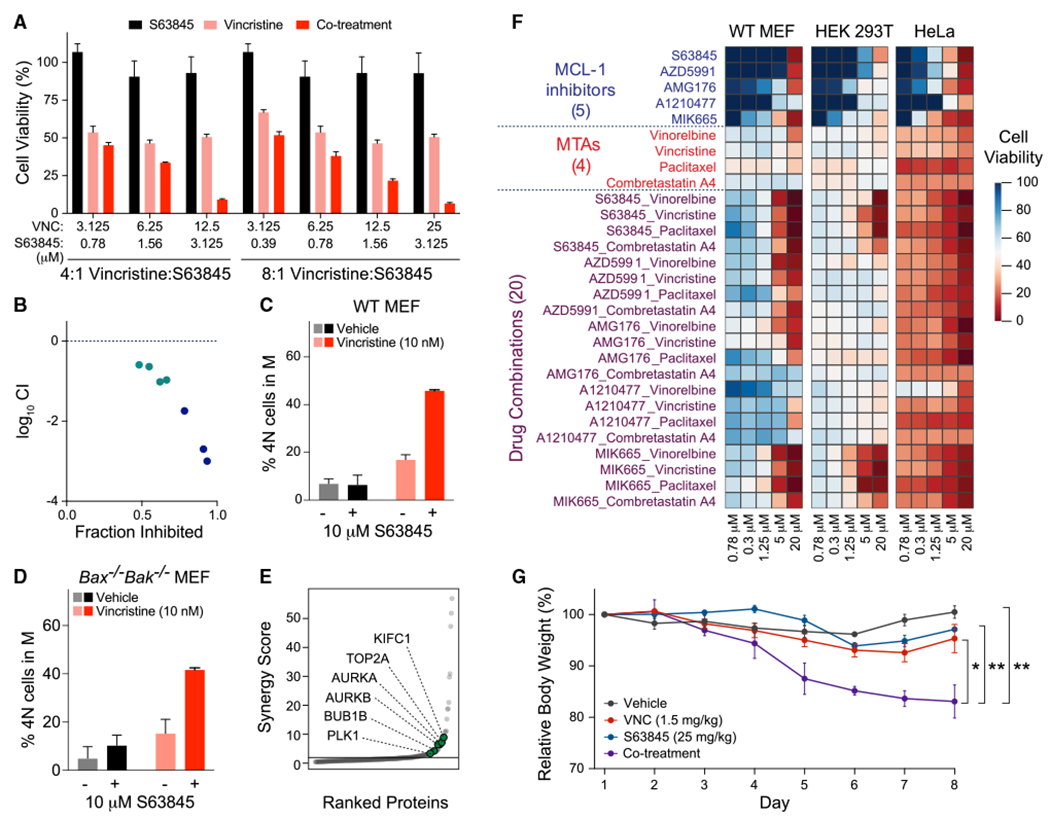
(A and B) Pharmacologic inhibition of MCL-1 by S63845 phenocopies Mcl-1 deletion in sensitizing wild-type MEFs to vincristine treatment (A), with Calcusyn analysis documenting a synergistic response (B). Data are mean ± SD for cell viability experiments (Cell TiterGlo assay) performed after 48 h of drug treatments in technical triplicate and conducted twice using independent preparations of cells and drugs with similar results.
(C and D) S63845 and vincristine combination treatment (16 h) caused mitotic arrest in wild-type MEFs (C), an effect that was independent of apoptosis, as demonstrated by replication of the finding in Bax−/−Bak−/− MEFs (D). Data are mean ± SD for experiments performed in technical duplicate and conducted twice using independent preparations of cells and drugs with similar results.
(E) Synergy scoring of protein abundances in wild-type MEFs treated with the S63845-vincristine combination for 16 h revealed selective upregulation of key proteins involved in the M phase, including KIFC1, TOP2A, AURKA, AURKB, BUB1, and PLK1.
(F) Enhanced cytotoxicity, as measured by Cell TiterGlo assay, upon combining a series of MCL-1 inhibitors and MTAs for 48 h of treatment, with relatively increased susceptibility in HeLa (cancer) cells compared with MEFs and HEK293T (non-cancer) cells. The heatmap was generated based on percent cell viability at the indicated doses, with experiments performed in technical triplicate.
(G) C57BL/6J 8-week-old female mice (n = 4 per arm) were treated intraperitoneally with either vehicle (PBS), S63845 (25 mg/kg) administered daily for 5 consecutive days, vincristine (1.5 mg/kg) administered once every 3 days (twice weekly), or the drug combination. Mice that received the drug combination demonstrated a statistically significant reduction in body weight compared with mice receiving vehicle or single-agent treatments. Error bars are mean ± SEM of body weights measured in four mice per treatment arm.
See also Figures S2N, S5, and S6.
